The intersection of olfactory science, microfluidics, and wearable technology has given rise to a novel category of personal protective equipment: masks with programmable scent diffusion. These advanced systems move beyond basic protection to enhance user experience through controlled aroma release, offering applications in stress reduction, cognitive enhancement, alertness maintenance, and even therapeutic intervention. For procurement specialists in healthcare, wellness, occupational safety, and consumer products, understanding how to source these sophisticated scent-delivery systems requires navigating a multidisciplinary landscape.
Masks with programmable scent diffusion are active delivery platforms that integrate micro-encapsulated fragrance reservoirs, precision micro-pumps or vaporizers, and control electronics to release specific scents at predetermined times, intensities, or in response to physiological or environmental triggers. This technology transforms masks from passive barriers into interactive devices that can improve wearer comfort, focus, or relaxation during extended use. Successful sourcing demands evaluation of scent formulation safety, delivery mechanism reliability, power efficiency, and user interface design.
The global market for aroma diffusion devices is projected to reach $5.8 billion by 2027, with wearable applications emerging as a high-growth niche. Research in Scientific Reports demonstrates that targeted scent delivery can reduce perceived stress during medical procedures by up to 30% and improve cognitive task performance by 15-20%. For applications ranging from high-stress healthcare environments to long-haul travel and industrial work, these masks offer a unique value proposition. Let's explore the key considerations for sourcing programmable scent-diffusing masks.
What Scent Formulation and Encapsulation Technologies Are Used?
The foundation of any scent-diffusing system is the aroma source itself. How scents are stored, stabilized, and activated determines the system's lifespan, safety, and effectiveness.
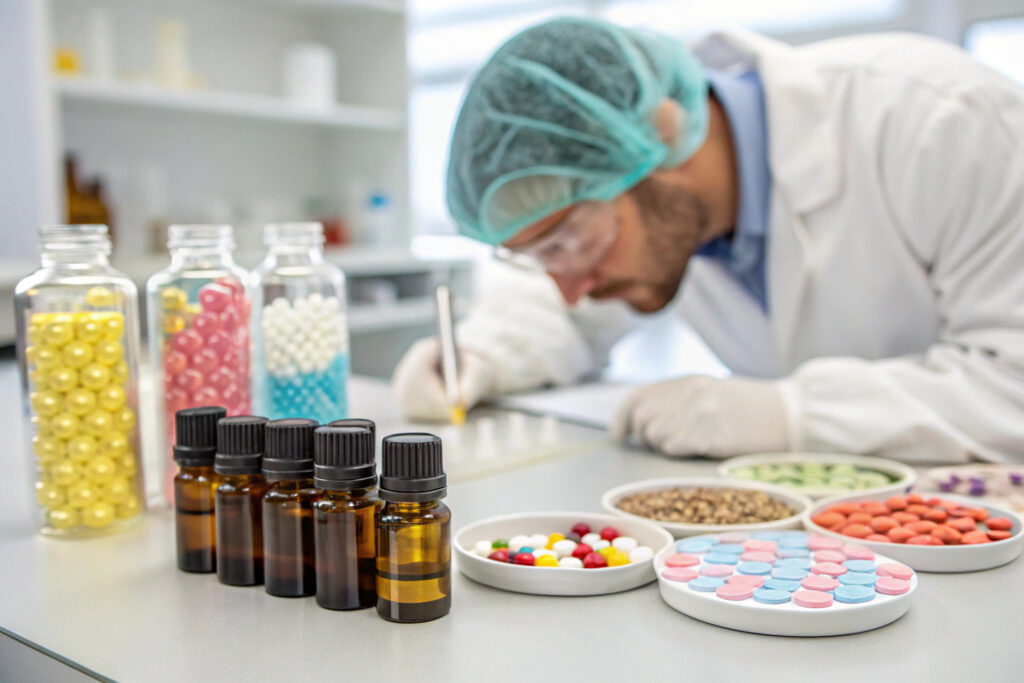

How Are Scents Stabilized and Controlled for Slow Release?
Pure essential oils or fragrance compounds evaporate quickly and are difficult to control. Advanced systems use encapsulation:
- Polymer Microcapsules: Fragrance oils are enclosed within microscopic shells of polymer (e.g., melamine-formaldehyde, gelatin). These capsules can be embedded in a fabric patch or contained in a cartridge. Release is triggered by mechanical rupture (e.g., from a piezoelectric actuator), heat, or moisture.
- Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes: These cage-like sugar molecules can encapsulate scent molecules within their hydrophobic cavity. The complex is stable and dry until exposure to humidity (like breath moisture), which triggers release. This allows for passive, breath-activated diffusion.
- Porous Carrier Materials: Scents are absorbed into high-surface-area materials like silica gel, zeolites, or specific polymers, from which they slowly desorb.
According to flavor and fragrance industry resources from Firmenich or Givaudan, micro-encapsulation can extend the active life of a scent from hours to weeks or months, depending on the trigger mechanism.
What Safety and Biocompatibility Standards Apply?
Any scent source in a mask must be safe for prolonged inhalation near the respiratory tract. Key considerations include:
- GRAS Status: "Generally Recognized As Safe" for inhalation, as defined by organizations like the Fragrance Materials Association (FMA).
- Non-Toxicity and Non-Allergenicity: Formulations must avoid common allergens and irritants. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for all components are essential.
- Carrier and Encapsulant Safety: The materials forming the capsules or carrier must also be biocompatible and not produce harmful byproducts when activated.
Sourcing should involve verification of safety certifications and possibly independent testing for respiratory tolerance, especially for masks intended for medical or all-day wear.
What Delivery Mechanisms Enable Precise, Programmable Release?
The "programmable" aspect hinges on the mechanism that releases the scent from its stored form into the inhaled airstream. Different mechanisms offer varying degrees of control, speed, and power efficiency.

How Do Micro-Pumps and Nebulizers Work for Liquid Scents?
For liquid fragrance reservoirs, delivery systems include:
- Piezoelectric Micropumps: Use a vibrating diaphragm to push precise nanoliter-to-microliter droplets of liquid scent into an airstream or onto a wick for evaporation. They offer excellent digital control over timing and dose.
- Ultrasonic or Piezoelectric Nebulizers: Create a fine, inhalable aerosol mist from a liquid reservoir. These provide rapid and noticeable scent delivery but may consume more power and require careful droplet size control to avoid wetting the mask interior.
- Micro-Peristaltic Pumps: Use rotating rollers to squeeze a flexible tube, delivering precise volumes. They are reliable for viscous formulations but can be slightly bulkier.
These active systems are ideal for complex programming (e.g., 10-minute lavender release at 2 PM) but require more power and electronics.
Can Passive or Low-Power Systems Be Programmable?
Yes, through smart material design. For example:
- Electrothermal Release: Scent is stored in a polymer matrix or on a pad. A tiny, low-power heating element (like a resistive wire) warms the pad to a specific temperature, accelerating the release rate of the scent without a pump. The "programming" controls the heating element's power and duration.
- Electro-Mechanical Rupture: An array of individually addressable micro-actuators (like tiny solenoids or piezoelectric benders) is placed over a field of microcapsules. The controller can trigger specific actuators to rupture chosen capsules, releasing a scent "pixel." This allows for blending scents on demand.
These approaches often offer a better balance between controllability and battery life for wearable devices.
What Control Systems and User Interfaces Are Required?
The user experience and practical utility depend on how the scent release is programmed and controlled. Interfaces range from simple pre-sets to smartphone-connected apps with biosensor integration.
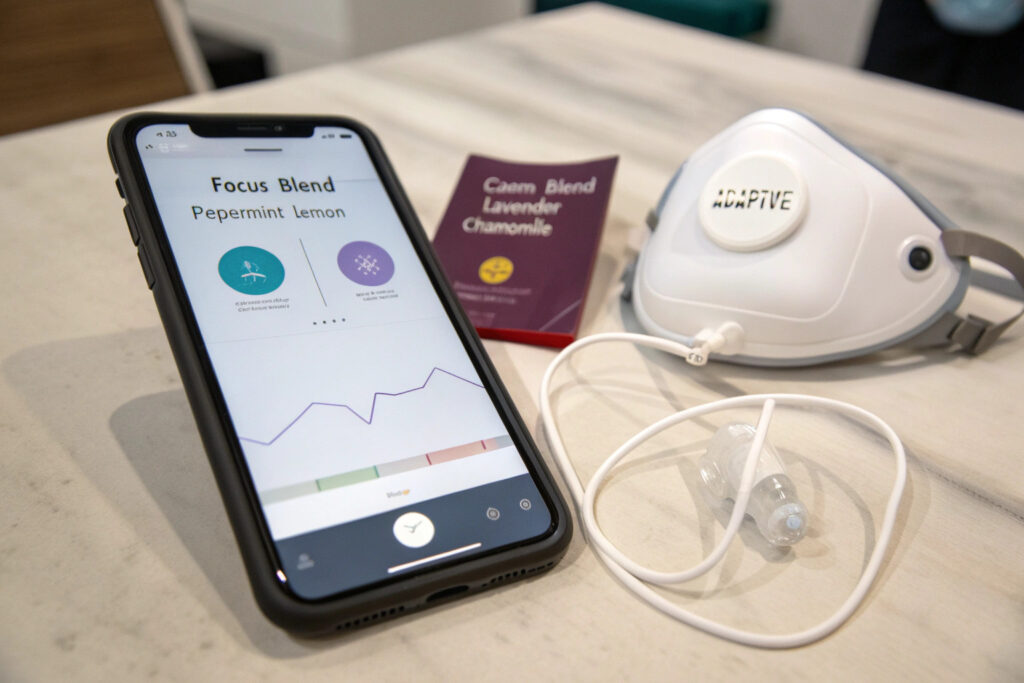

What Are Common Programming Paradigms?
- Time-Based Scheduling: The user or an administrator programs specific release times (e.g., a calming scent before a known stressful event, an alerting scent during post-lunch drowsiness).
- Manual On-Demand: A simple button on the mask or a tap in a smartphone app triggers a short burst of scent.
- Physiologically-Triggered (Biofeedback): The mask integrates or connects with sensors (e.g., heart rate variability monitor, galvanic skin response) to detect stress or fatigue and automatically release an appropriate scent to counteract it. This is the frontier of adaptive wellness technology.
- Environmental-Triggered: Using onboard sensors (e.g., microphone for noise level, gas sensor for malodors) to trigger scent release in response to the environment.
How is Power Managed for All-Day Wear?
Scent delivery, especially active pumping or heating, consumes power. Effective systems implement:
- Efficient Duty Cycling: The delivery mechanism only activates for seconds at a time.
- Low-Power Microcontrollers and Bluetooth LE: For connectivity and control.
- Energy-Aware Scheduling: The software avoids depleting the battery with unnecessary releases.
A typical target for a consumer device is 8-12 hours of use with a small, rechargeable lithium-polymer battery. Sourcing should include reviewing power consumption specs and battery life claims under realistic use patterns.
What Are the Primary Application Sectors and Use Cases?
Understanding the intended application is crucial for specifying the right features, safety level, and form factor when sourcing.
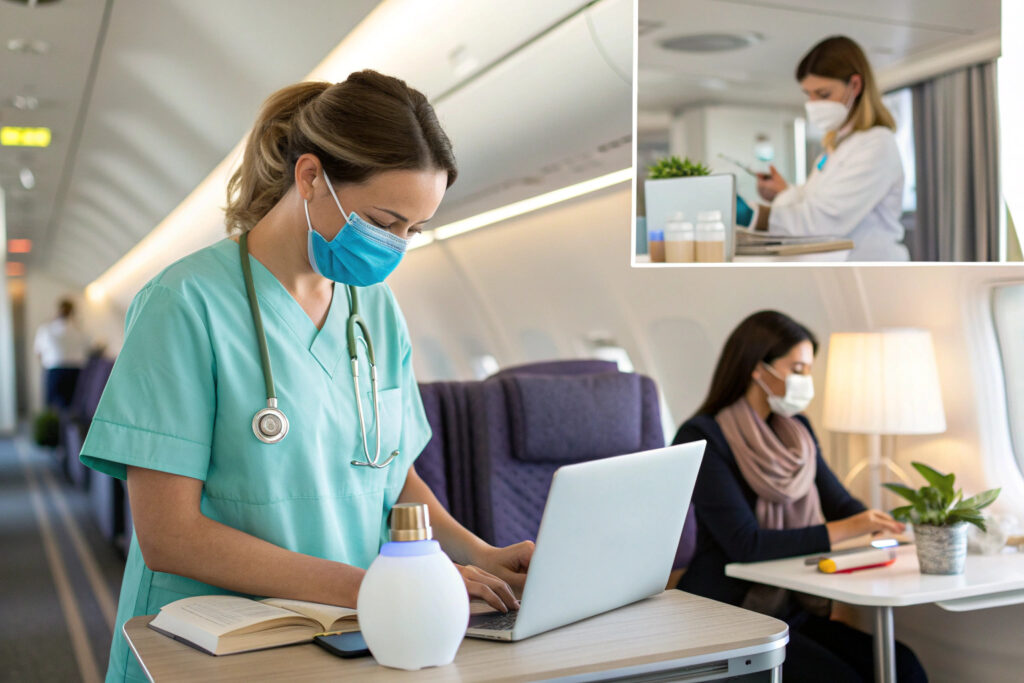

How Are These Masks Used in Healthcare and Workplace Settings?
- Healthcare: For staff facing long, stressful shifts—releasing calming scents (lavender, bergamot) to reduce burnout or alerting scents (peppermint, rosemary) during long, tedious tasks. For patients, they can aid in anxiety reduction before procedures.
- Industrial & Safety: In environments with unpleasant occupational odors (waste management, chemical plants), a clean, pleasant scent can improve comfort. In safety-critical roles, alertness scents can help maintain concentration.
- Therapeutic: As part of prescribed therapy for anxiety, PTSD, or insomnia, under medical guidance.
For these settings, sourcing must prioritize robust construction, easy decontamination, and compatibility with other protective equipment (like goggles).
What is the Consumer Wellness and Lifestyle Market?
This includes masks for:
- Travel: Combating fatigue and stale air in planes or airports.
- Focus & Productivity: For students or professionals working in shared or distracting environments.
- Sleep & Relaxation: Incorporating scents known to promote relaxation for use at home or during travel.
Here, aesthetics, comfort, and intuitive app design become as important as technical performance.
What Validation and Performance Metrics Matter?
Unlike a standard mask, a scent-diffusing mask is a combination of a medical/wellness device and a consumer electronics product. Its performance should be measured accordingly.

How is Olfactory Performance Quantified?
- Release Consistency: Measured by the mass or volume of fragrance released per activation (using micro-scales or chemical analysis), ensuring dose uniformity.
- Sensory Threshold and Intensity: Determining the minimum release amount perceptible to users and mapping the relationship between release volume and perceived intensity.
- Temporal Dynamics: How quickly the scent is perceived after activation and how long it lingers.
These tests often follow adapted methods from the field of sensory science and consumer product testing.
What are the Reliability and Safety Tests?
- Cycle Testing: The delivery mechanism (pump, heater, actuator) is activated thousands of times to ensure it doesn't fail or degrade in performance.
- Leak and Contamination Testing: Ensuring the fragrance liquid or vapor cannot leak into unintended parts of the mask or cause skin irritation.
- Electrical and Battery Safety: Compliance with relevant consumer electronics safety standards (e.g., IEC 62368-1).
- Long-Term Stability: Testing scent cartridges for degradation over time, especially under varying temperature and humidity conditions.
Conclusion
Sourcing masks with programmable scent diffusion requires a holistic evaluation of the scent source's safety and stability, the precision and reliability of the delivery mechanism, the intuitiveness of the control system, and the validation of both olfactory and technical performance. The most viable systems will seamlessly integrate these elements into a comfortable, wearable form factor suitable for their target environment—be it a hospital, airplane, or office. As this field grows, we can expect more sophisticated biofeedback integration and personalized scent profiles, making these devices powerful tools for managing psychological state and enhancing well-being in demanding environments.
Ready to explore how programmable scent diffusion can enhance your mask products or wellness offerings? Contact our Business Director, Elaine, at elaine@fumaoclothing.com to discuss sourcing options, OEM development, or customizing this innovative technology for your specific application needs.