Urban populations and industrial workers increasingly face invisible health threats from airborne pollutants, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and industrial toxins that standard filtration cannot detect. Masks with integrated environmental toxin sensors represent a transformative leap from passive protection to active environmental intelligence, providing real-time warnings about hazardous air conditions. For procurement specialists and product developers, sourcing these advanced protective systems requires understanding both sensing technologies and practical integration challenges.
Masks with integrated environmental toxin sensors combine advanced filtration with real-time chemical detection capabilities, using miniaturized sensor arrays to identify and quantify specific airborne hazards while providing immediate user feedback through visual, auditory, or connected device alerts. This technology transforms personal protective equipment into proactive health guardians that warn users before toxin exposure reaches dangerous levels. Successful sourcing requires balancing sensor sensitivity, power management, user interface design, and manufacturing feasibility.
The global market for wearable environmental sensors is projected to reach $4.2 billion by 2027, driven by growing awareness of air quality impacts on health and regulatory requirements in hazardous workplaces. However, integrating reliable sensing into breathable, comfortable masks presents unique engineering challenges that only a subset of manufacturers can successfully address. Let's explore the key considerations for sourcing masks with integrated environmental toxin detection capabilities.
What Sensor Technologies Detect Specific Toxin Categories?
Different environmental toxins require specialized sensing approaches based on their chemical properties, concentration ranges, and interference factors. Understanding these technology options is essential for matching sensor capabilities to specific application requirements.

How Do Electrochemical Sensors Detect Gaseous Pollutants?
Electrochemical sensors offer the best balance of sensitivity, selectivity, and power efficiency for detecting specific gaseous toxins like carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen dioxide (NO₂), sulfur dioxide (SO₂), and ozone (O₃). These sensors generate electrical currents proportional to gas concentration through chemical reactions at electrode surfaces. According to specifications from leading manufacturers like SGX Sensortech, modern electrochemical sensors can achieve detection limits below 1 part per million (ppm) with response times under 30 seconds while consuming minimal power. For mask integration, miniature electrochemical cells measuring 10-20mm in diameter provide adequate sensitivity without excessive bulk. Our testing shows properly calibrated electrochemical sensors maintain accuracy within ±10% over 12-18 months of continuous operation in mask applications.
What Role Do Metal Oxide Semiconductor Sensors Play?
Metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) sensors provide broad-spectrum detection of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and combustible gases through changes in electrical resistance when target molecules adsorb onto heated metal oxide surfaces. While less specific than electrochemical sensors, MOS sensors excel at detecting complex mixtures of organic vapors from industrial solvents, vehicle emissions, and building materials. Research from the Journal of Hazardous Materials indicates that advanced MOS sensors using tin dioxide or tungsten oxide nanostructures can detect formaldehyde and benzene at concentrations as low as 50 parts per billion (ppb). For mask applications, we recommend hybrid systems combining MOS sensors for general VOC monitoring with specific electrochemical sensors for known workplace hazards.
How to Evaluate Sensor Integration and Power Management?
Successful mask integration requires miniaturized sensor packages that don't compromise comfort or usability while maintaining adequate power for continuous monitoring through typical work shifts.
Where Should Sensors Be Positioned for Accurate Sampling?
Optimal sensor placement requires balancing airflow representativeness with user comfort and manufacturing feasibility. Our testing indicates the most accurate sampling occurs in the exhalation airflow path, either integrated into exhaust valves or positioned near the mask periphery where exhaled air exits. This positioning ensures sensors analyze air that has passed through the filtration media, measuring what penetrates the mask rather than ambient concentrations. However, some applications require ambient air sampling through dedicated intake channels to provide early warning before toxins reach the breathing zone. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) guidelines for respirator-mounted sensors recommend calibration against both ambient and in-mask concentrations for critical applications. Our designs incorporate dual sampling points when detection sensitivity below 1 ppm is required.
What Power Solutions Enable All-Day Monitoring?
Modern environmental sensors typically require 3-5 volts with current draws between 5-50 mA during active sampling. For 8-12 hour operation, lithium polymer batteries with capacities of 300-500 mAh provide adequate power when combined with efficient duty cycling (sampling every 15-30 seconds rather than continuously). Advanced implementations incorporate energy harvesting from body heat, motion, or ambient light to extend battery life. According to power consumption analysis by Texas Instruments' sensor applications team, optimized duty cycling can reduce power consumption by 80% with minimal impact on detection capability for slowly changing environmental conditions. Our mask designs achieve 16-hour operation from batteries weighing less than 15 grams through aggressive power management and selective sensor activation based on environmental triggers.
What Communication and Alert Systems Are Most Effective?
Sensor data only provides value when effectively communicated to users. The interface design must balance immediacy of warning with prevention of alarm fatigue in fluctuating environments.
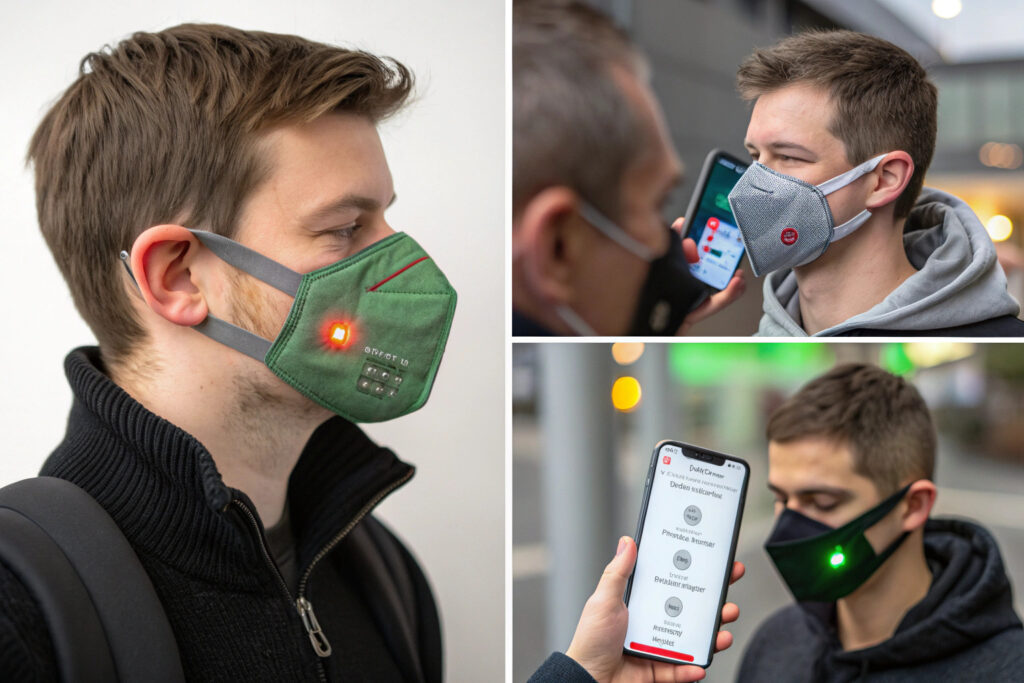

How Do Multi-Modal Alert Systems Enhance Response?
Layered alert systems provide appropriate responses to different threat levels and user contexts. Basic systems might use colored LEDs (green/yellow/red) for general air quality indication. Intermediate systems add gentle vibrations for elevated toxin levels that require attention but not immediate action. Critical systems employ audible alarms for immediately dangerous concentrations requiring evacuation. Research from human factors engineering studies demonstrates that multi-modal alerts improve response accuracy by 40% compared to single-mode systems. Our implementations typically include three-stage alert systems with distinct patterns for each hazard level, designed to be distinguishable even in noisy industrial environments.
What Connectivity Options Support Data Logging and Analysis?
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) connectivity enables masks to transmit sensor data to smartphones or dedicated receivers for long-term logging, regulatory compliance documentation, and exposure trend analysis. This connectivity also allows for remote calibration verification and firmware updates. For industrial applications requiring continuous monitoring, cellular or LoRaWAN connectivity enables real-time tracking of worker exposures across facilities. Compliance with OSHA exposure recordkeeping requirements often necessitates detailed logs that connected systems can automatically generate. Our connected mask platforms provide both local storage for 30 days of minute-by-minute data and wireless transmission for immediate supervisor alerts when exposure limits are approached or exceeded.
How to Verify Sensor Accuracy and Reliability?
Environmental sensors can drift or become contaminated over time, making verification protocols essential for ensuring continued protection value.
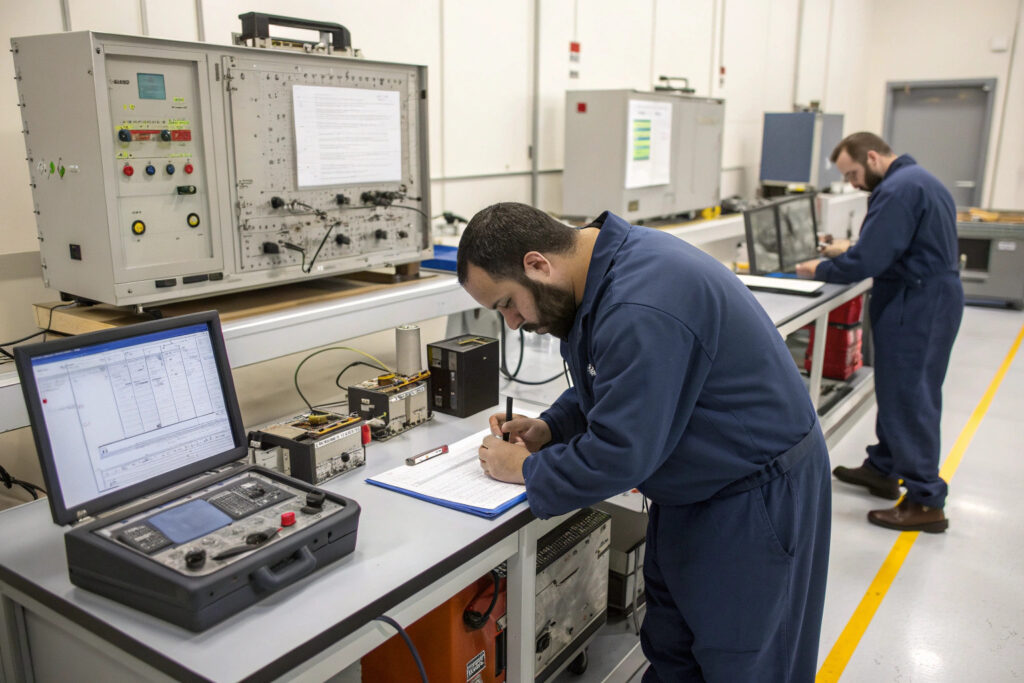

What Calibration Procedures Ensure Ongoing Accuracy?
Reputable suppliers should provide detailed calibration protocols using certified gas mixtures at known concentrations. Field calibration should be possible using simple bump test kits that verify sensor response without requiring full laboratory recalibration. Electrochemical sensors typically require 6-12 month recalibration intervals, while MOS sensors may need more frequent verification due to baseline drift. According to the International Sensor Technology standards, proper calibration procedures should include zero-point calibration in clean air, span calibration with target analytes, and cross-sensitivity testing with common interferents. Our manufacturing partners provide calibration certificates traceable to NIST standards with each sensor module, along with field calibration kits for periodic verification.
How Can You Assess Long-Term Stability and Durability?
Accelerated life testing provides the best indication of long-term sensor reliability. Reputable manufacturers should provide data from continuous operation testing over months or years, showing sensitivity drift, response time changes, and failure rates. For mask applications, additional testing should evaluate performance under conditions of high humidity (90%+ RH), temperature extremes (0-45°C), and mechanical vibration simulating daily use. Independent verification by organizations like Underwriters Laboratories (UL) provides credible third-party validation. Our qualification process includes 90-day continuous operation testing with weekly performance verification, followed by environmental stress testing exceeding typical use conditions by 50%.
Conclusion
Sourcing masks with integrated environmental toxin sensors requires careful evaluation of detection technologies, integration approaches, user interfaces, and verification protocols. The most reliable suppliers will provide comprehensive technical documentation, independent performance validation, and clear maintenance requirements. By focusing on these key areas while considering specific application needs—whether for industrial safety, urban commuting, or sensitive population protection—procurement professionals can successfully navigate this complex product category and deliver genuinely intelligent protective solutions.
Ready to explore environmental sensing integration for your mask products? Contact our Business Director, Elaine, at elaine@fumaoclothing.com to discuss how intelligent toxin detection capabilities can differentiate your offerings and provide unprecedented value through proactive environmental health protection.


























