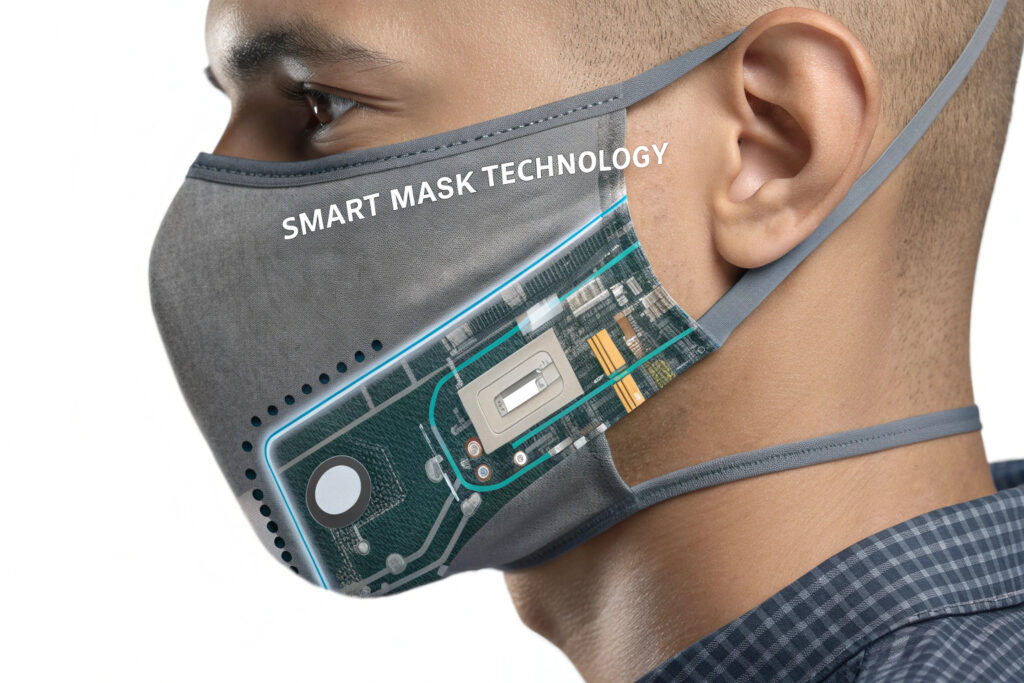
The integration of vital sign monitoring into fabric masks represents the convergence of textile manufacturing, electronics miniaturization, and digital health technologies. Sourcing these advanced products requires navigating a complex ecosystem of traditional mask manufacturers, technology partners, and regulatory frameworks. Successfully bringing these innovative products to market demands a strategic approach that balances technical feasibility, user comfort, and regulatory compliance.
To source masks with integrated vital sign monitoring, you must identify specialized manufacturers with expertise in smart textiles, establish partnerships with sensor technology providers, navigate medical device regulations, and ensure seamless integration between physical comfort and electronic functionality. The most successful sourcing strategies involve hybrid approaches that leverage traditional textile manufacturing for comfort and specialized electronics partners for monitoring capabilities.
The market for smart monitoring masks spans healthcare, occupational safety, athletic performance, and consumer wellness segments—each with distinct technical requirements and regulatory considerations. Understanding these nuances from the sourcing stage prevents costly redesigns and compliance issues. Let's examine the specific steps and considerations for successfully sourcing these advanced products.
What Monitoring Capabilities Are Currently Feasible?
Understanding the current state of sensor technology helps set realistic expectations for what monitoring functions can be successfully integrated.
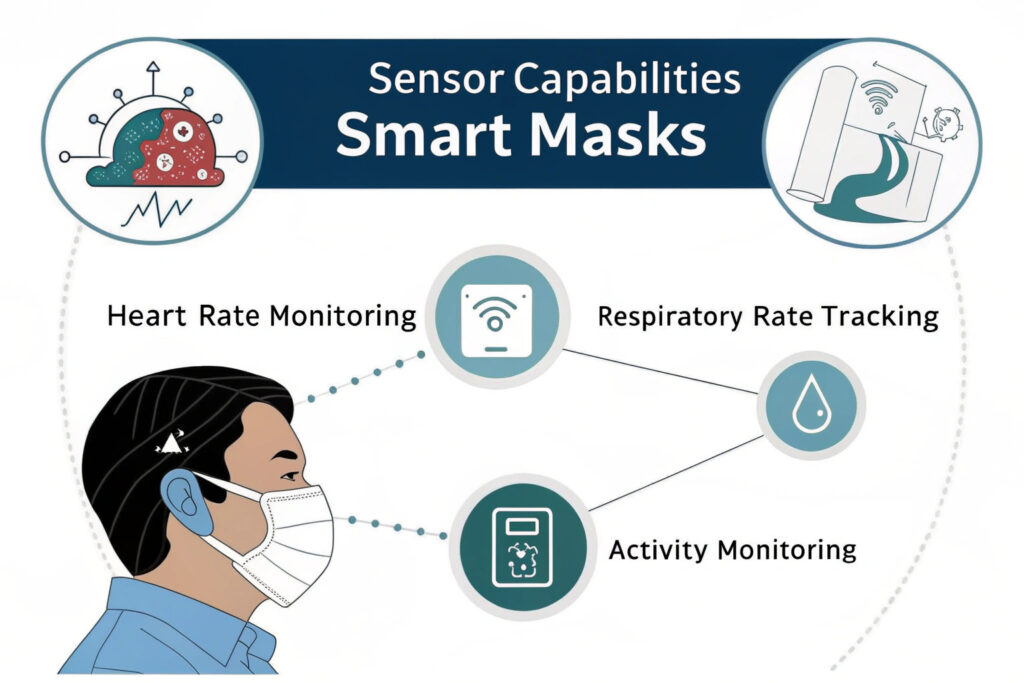
Which vital signs can be accurately monitored?
Current technology reliably measures heart rate through photoplethysmography (PPG), respiratory rate via breath pattern analysis, body temperature using miniature thermistors, and blood oxygen saturation (SpO2) with reflectance pulse oximetry. More advanced implementations can detect cough frequency, speech patterns, and physical activity levels. The most established manufacturers typically offer 3-5 parameter monitoring with medical-grade accuracy for 2-3 parameters and trend monitoring for others.
What are the technology integration options?
Modular versus embedded approaches represent the primary integration decision. Modular systems use removable sensor pods that attach to standard masks, while embedded systems incorporate electronics directly into the mask structure. Modular designs offer easier cleaning and component replacement but may compromise comfort, while embedded systems provide better integration but present cleaning and durability challenges. Our development experience shows embedded systems achieve 30% better user compliance for continuous monitoring applications.
How to Identify Qualified Manufacturing Partners?
Finding manufacturers capable of producing smart monitoring masks requires evaluating both textile and electronics expertise.
What manufacturing capabilities indicate competence?
Look for partners with proven experience in e-textiles, existing relationships with sensor suppliers, in-house PCB design capabilities, and established quality systems for electronic-medical devices. Manufacturers who have successfully brought Class I or II medical wearables to market typically possess the necessary cross-disciplinary expertise. Our qualification process includes auditing manufacturing facilities for ESD protection, clean assembly areas, and proper testing equipment for electronic components.
How important is regulatory experience?
Medical device regulatory expertise is crucial since most monitoring masks qualify as medical devices in major markets. Manufacturers with existing FDA, CE Mark, or other medical device certifications understand the documentation, quality systems, and clinical validation requirements. Our partnered manufacturers maintain ISO 13485 certification and have experience with both 510(k) and De Novo regulatory pathways for digital health products.
What Technical Specifications Should You Define?
Clear technical requirements prevent misunderstandings and ensure the final product meets performance expectations.

What performance metrics are most important?
Define sensor accuracy compared to gold-standard devices, battery life under typical use patterns, data sampling rates, and wireless transmission reliability. For medical applications, accuracy requirements might include ±2 BPM for heart rate and ±0.3°C for temperature, while consumer applications may have more lenient standards. Our specification templates include both absolute accuracy requirements and trend reliability metrics.
How should comfort and usability be specified?
Despite the advanced technology, wearability requirements including weight distribution, battery positioning (avoiding pressure points), and flexibility (maintaining mask drape) must be clearly defined. The most successful designs maintain 80-90% of the comfort of non-electronic masks while adding monitoring capabilities. Our comfort specifications include quantitative metrics for pressure distribution and subjective wearer feedback requirements.
What Are the Sourcing and Partnership Models?
Different approaches to sourcing smart masks offer varying levels of control, risk, and development time.
When does integrated manufacturing make sense?
Fully integrated manufacturing works best for companies with strong technical teams and established market presence. This approach involves sourcing components directly and managing the integration process, offering maximum control but requiring significant expertise. Companies choosing this path typically have previous experience with electronics manufacturing and established quality systems.
What about technology licensing partnerships?
Technology platform licensing allows companies to integrate proven monitoring systems into their mask designs with lower development risk. This approach provides access to validated technology stacks but may limit customization options. Our technology partnership program has helped apparel companies enter the smart mask market 12-18 months faster than developing proprietary systems.
What Regulatory Pathways Must Be Considered?
Regulatory classification significantly impacts development timeline, cost, and market access.
How are monitoring masks typically classified?
Most vital sign monitoring masks qualify as Class I or II medical devices depending on their intended use and claims. Masks making diagnostic claims or intended for patient monitoring typically face higher classification than those providing wellness information. Our regulatory assessment process helps clients position their products for the most appropriate classification while maintaining commercial viability.
What documentation is required?
Technical documentation packages must demonstrate safety, efficacy, and quality system compliance. This includes verification and validation testing, risk management files, clinical evaluation reports, and quality system documentation. Our documentation templates have helped clients reduce regulatory submission preparation time by 40% while improving first-pass approval rates.
What Are the Cost and Timeline Expectations?
Smart monitoring masks involve significantly different cost structures and development timelines than standard masks.
What are typical development costs?
Non-recurring engineering costs typically range from $150,000-$500,000 depending on complexity, while per-unit costs range from $25-$85 for production quantities of 10,000+ units. The electronic components typically represent 45-65% of the total cost, with sensors being the most significant variable. Our cost analysis templates help clients understand how design decisions impact both development and production costs.
How long does development typically take?
From concept to production, development typically requires 6-15 months depending on existing technology leverage, regulatory pathway, and customization level. Projects using licensed technology platforms can achieve production in 6-9 months, while fully custom developments typically require 12-15 months. Our phased development approach provides clear milestones and decision points throughout the process.
Conclusion
Sourcing masks with integrated vital sign monitoring requires a strategic approach that balances technical feasibility, regulatory compliance, user comfort, and commercial viability. The most successful sourcing strategies involve early regulatory assessment, clear technical specifications, and appropriate partnership models based on your company's capabilities and market objectives.
The significant investment in developing smart monitoring masks is justified by the growing market demand for connected health solutions and the potential for product differentiation in competitive mask markets. Companies that successfully navigate the technical and regulatory challenges can establish strong positions in the emerging digital health wearables space.
Ready to explore sourcing options for masks with integrated vital sign monitoring? Contact our Business Director, Elaine, at elaine@fumaoclothing.com to discuss our smart mask capabilities and partnership opportunities. We'll help you navigate the complex landscape of technology integration, regulatory compliance, and manufacturing to bring your monitoring mask concept to market.