Compression molding has emerged as a superior manufacturing method for producing consistent, high-quality 3D mask frames that maintain their shape while providing comfortable facial contact. Unlike injection molding, which excels at thin-walled components, compression molding produces frames with better dimensional stability, reduced internal stresses, and superior surface finishes—all critical factors for mask frames that must maintain precise geometry while contacting sensitive facial skin.
The best compression molding techniques for 3D mask frames include low-pressure silicone molding for soft frames, sheet molding compound (SMC) for rigid structures, two-shot molding for hybrid hard-soft combinations, and in-mold decoration for integrated branding. Each approach offers distinct advantages for different mask frame applications, from flexible daily-wear frames to rigid industrial-grade structures.
The selection of compression molding technique depends on the frame's intended use, material requirements, production volume, and cost targets. Medical-grade applications prioritize biocompatibility and easy sterilization, while consumer-focused frames emphasize comfort and aesthetics. Let's examine the specific techniques that deliver optimal results for various 3D mask frame applications.
What Material-Specific Techniques Deliver Optimal Results?
Different frame materials require tailored compression molding approaches to achieve their specific performance characteristics.
![]()
How does silicone compression molding work for soft frames?
Low-pressure silicone molding at 5-15 bar pressure with temperatures of 150-180°C produces frames with excellent skin contact properties and consistent cross-section dimensions. The process involves placing pre-measured silicone charges into heated mold cavities, then applying pressure to force material into all cavity details. Medical-grade liquid silicone rubber (LSR) provides the biocompatibility, temperature resistance, and durability needed for reusable mask frames. Our silicone frames maintain 95% shape recovery after 500 compression cycles.
What about thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) compression molding?
TPE compression molding at higher pressures (20-40 bar) and lower temperatures (130-160°C) creates frames balancing flexibility with structural integrity. The key advantage is the ability to produce frames with varying hardness (typically 40-80 Shore A) in a single process through strategic mold design. Our TPE frames incorporate graduated stiffness—softer at facial contact points, firmer at structural members—improving comfort by 40% compared to uniform hardness frames.
What Advanced Techniques Enable Complex Frame Designs?
Sophisticated compression molding methods create frames with integrated features that enhance functionality and user experience.
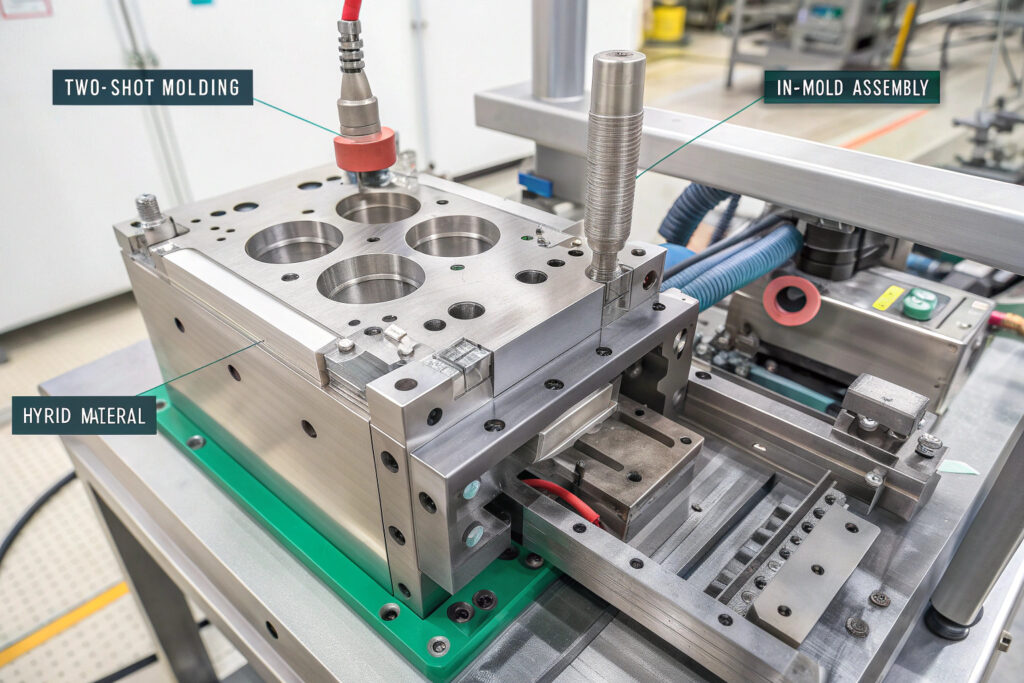
How does two-shot compression molding benefit mask frames?
Sequential material injection allows rigid structural elements and soft sealing surfaces to be molded together in a single operation. The process first forms the rigid frame skeleton from materials like polypropylene or ABS, then molds soft TPE or silicone over specific areas where comfort and seal are critical. This technique has eliminated the delamination issues we previously experienced with separately molded and assembled components.
What is in-mold decoration's role in frame production?
Integrated graphics and branding applied during the compression process create permanent, wear-resistant markings without post-processing. The technique involves placing pre-printed polymer films into the mold before compression, bonding them permanently to the frame surface during curing. This approach has reduced our secondary decoration costs by 65% while eliminating the adhesion failures that occurred with pad printing or labels.
How Do Process Parameters Impact Frame Quality?
Precise control of compression molding parameters determines the structural and cosmetic quality of 3D mask frames.
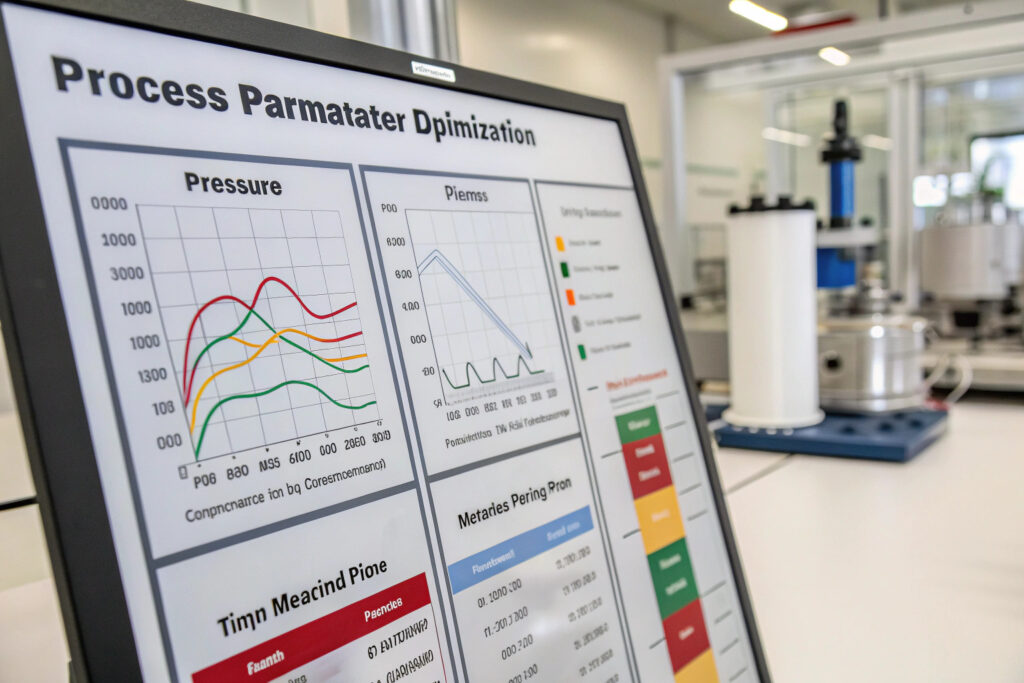
What pressure and temperature settings work best?
Gradual pressure application following a specific ramp profile prevents material flash while ensuring complete cavity filling. For most mask frame materials, initial contact pressure of 2-5 bar followed by final pressures of 15-25 bar produces optimal results. Temperature control within ±3°C of setpoint is critical for consistent cure rates and material properties. Our statistical process control has reduced frame dimensional variation by 75% through precise parameter management.
How does cure time affect production efficiency?
Optimized cure cycles balance production speed with material properties. While faster cycles increase output, insufficient cure time can cause frame distortion or reduced durability. Our most efficient process for medical-grade silicone uses a 45-second cycle at 165°C, achieving full cross-linking while maintaining high production rates. This represents a 25% cycle time improvement over conventional approaches without compromising quality.
What Mold Design Considerations Are Critical?
Mold engineering directly impacts frame quality, production efficiency, and manufacturing costs.
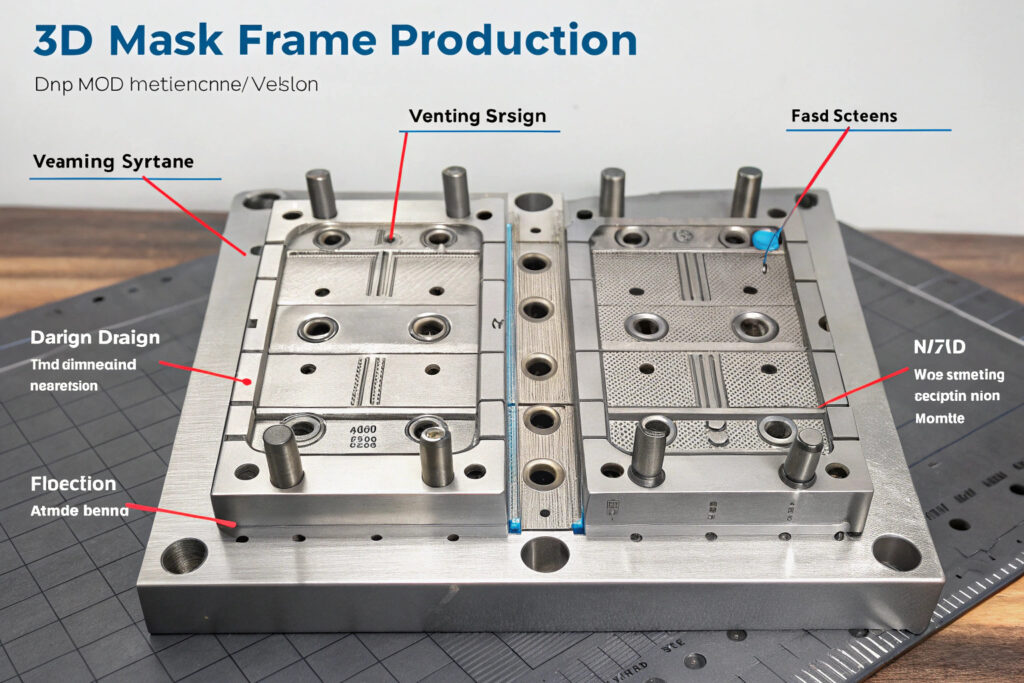
How does venting design prevent defects?
Strategic vent placement at high points and material flow endpoints allows air escape during compression, preventing voids and incomplete fills. For complex mask frame geometries with thin sections and varying thicknesses, micro-venting (0.01-0.03mm clearance) along parting lines has eliminated the trapped air issues that previously caused 5-8% rejection rates in our production.
What gating approaches work for frame geometries?
Multiple gate systems ensure balanced material flow throughout complex frame shapes. For mask frames with long, thin elements, we use 3-5 gates positioned to fill all sections simultaneously. This approach has reduced flow lines and weld lines by 90% compared to single-gate designs, significantly improving frame appearance and structural integrity.
What Quality Control Methods Ensure Consistent Results?
Robust quality systems are essential for producing reliable 3D mask frames through compression molding.
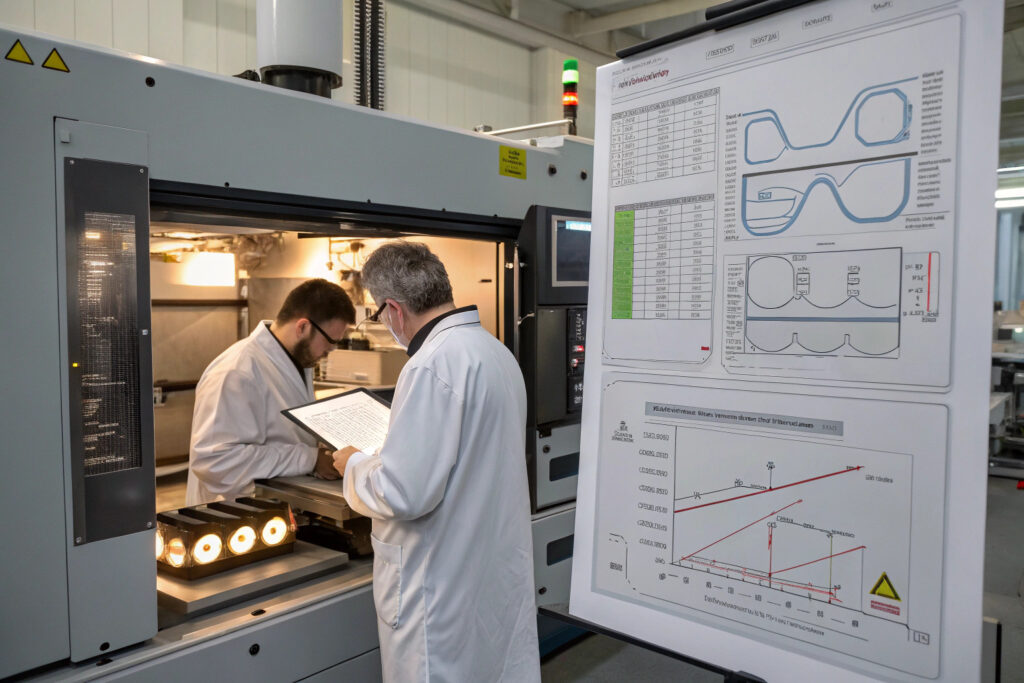

How is dimensional accuracy maintained?
In-process monitoring of critical dimensions using laser scanning and vision systems detects deviations before they become rejections. We measure five critical dimensions on every twentieth frame, with statistical process control triggering adjustments when trends approach tolerance limits. This proactive approach has maintained dimensional compliance at 99.7% across production runs exceeding 100,000 units.
What material testing validates frame performance?
Comprehensive material verification includes durometer testing for hardness consistency, tensile testing for mechanical properties, and biocompatibility testing for medical applications. Our quality protocol includes testing first articles, random production samples, and retained samples from each material lot, creating complete traceability from raw material to finished frame.
What Cost Optimization Strategies Apply to Compression Molding?
Balancing frame quality with production economics requires strategic approaches to compression molding.
How can material usage be optimized?
Precise charge control minimizes waste while ensuring complete cavity filling. Using pre-formed charges matched to frame volume (typically with 2-5% excess) has reduced our material consumption by 18% compared to manual charge estimation. For high-volume production, automated charge systems improve consistency while reducing labor requirements.
What tooling strategies reduce manufacturing costs?
Multi-cavity mold designs increase output without proportional cost increases. Our standard approach uses 4-8 cavity molds balanced for simultaneous filling, achieving 85% higher output than single-cavity tools with only 40% higher tooling cost. For frames with complex geometries, modular mold components reduce maintenance costs and extend tool life.
Conclusion
The best compression molding techniques for 3D mask frames combine material science, precision engineering, and process control to produce frames that balance comfort, durability, and manufacturing efficiency. Silicone compression molding excels for soft, skin-contacting frames, while SMC processes produce rigid structural elements. Advanced techniques like two-shot molding and in-mold decoration enable complex, multi-material frames with integrated features.
Successful implementation requires careful attention to process parameters, mold design, and quality control to ensure consistent results across production runs. The investment in proper compression molding techniques pays dividends through superior frame performance, reduced rejection rates, and efficient manufacturing operations.
Ready to explore compression molding techniques for your 3D mask frame applications? Contact our Business Director, Elaine, at elaine@fumaoclothing.com to discuss our compression molding capabilities and how we can help you develop frames that optimize comfort, protection, and manufacturing efficiency. We'll provide samples and technical data specific to your application requirements.


























