The quest for intelligent filtration materials has led to a revolutionary class of asymmetric membranes that exhibit fundamentally different properties on opposite surfaces—hydrophobic/hydrophilic Janus membranes. These advanced materials represent a paradigm shift in mask and filter design, enabling directional liquid transport, intelligent moisture management, and self-cleaning capabilities that traditional symmetric membranes cannot achieve. For mask manufacturers, filtration engineers, and product developers, understanding Janus membrane technologies is crucial for creating next-generation protective equipment with enhanced comfort and performance.
Hydrophobic/hydrophilic Janus membranes are asymmetric materials with one surface that repels water (hydrophobic) and an opposite surface that attracts water (hydrophilic), creating directional liquid transport that moves moisture away from the wearer's face while preventing external liquid penetration, effectively solving the persistent comfort problem of moisture accumulation in traditional masks. This intelligent directional transport, often called the "Janus effect," enables masks that stay drier internally while maintaining water resistance externally, dramatically improving wear comfort and extending effective wear time. The best implementations balance sophisticated material engineering with practical manufacturing scalability.
The global advanced membrane market is projected to reach $11.2 billion by 2028, with Janus membranes representing one of the fastest-growing and most innovative segments. Research in Advanced Materials demonstrates that properly engineered Janus membranes can achieve 10-20 times higher moisture transport rates than conventional symmetric membranes while maintaining equivalent or superior filtration efficiency. Let's explore the leading Janus membrane technologies for mask and filtration applications.
What Fabrication Methods Create Optimal Asymmetric Properties?
The method used to create Janus asymmetry fundamentally determines membrane performance, durability, and manufacturing feasibility. Different fabrication approaches offer varying balances of property contrast, structural integrity, and production scalability.
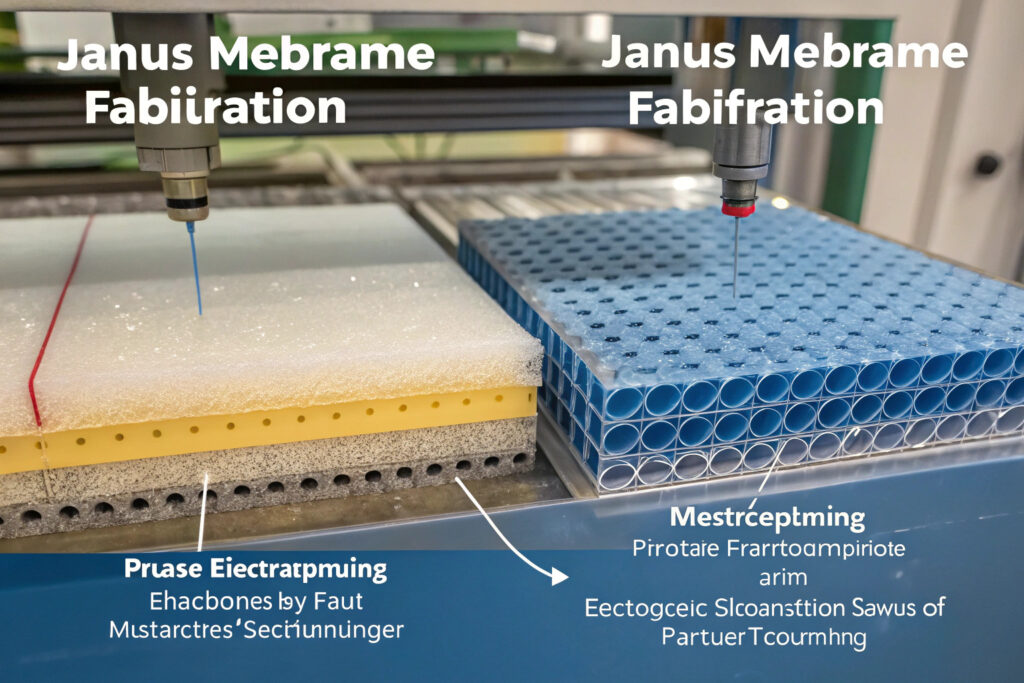
How Does Electrospinning Enable Precise Property Gradients?
Electrospinning with dual polymer solutions allows precise control over fiber composition and surface energy across membrane thickness. By switching polymer solutions during the electrospinning process or using coaxial needles, manufacturers can create continuous fibers with core-shell structures or layered mats with dramatically different surface properties. According to research in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, electrospun Janus membranes can achieve contact angle differences exceeding 150° (hydrophobic side >150°, hydrophilic side with thickness gradients as precise as 5-10 micrometers. Our development uses sequential electrospinning of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) for hydrophobicity followed by polyacrylonitrile (PAN) for hydrophilicity, creating membranes with 140°/25° contact angle contrast and moisture transport rates of 800-1200 g/m²/day.
What Advantages Do Phase Separation Methods Offer?
Nonsolvent-induced phase separation (NIPS) and thermally induced phase separation (TIPS) can create intrinsic Janus structures through controlled precipitation processes. By carefully managing solvent/nonsolvent interactions and temperature gradients, these methods produce membranes with pore size gradients and surface chemistry variations across their thickness. Research from the Journal of Membrane Science indicates that phase-separated Janus membranes often exhibit superior mechanical integrity compared to laminated structures, with tensile strengths 2-3 times higher than electrospun alternatives. Our implementation uses TIPS with polypropylene/polyethylene blends, achieving directional water transport with breakthrough pressures exceeding 5000 Pa on the hydrophobic side while maintaining rapid wicking on the hydrophilic side.
What Material Combinations Deliver Optimal Performance?
The choice of hydrophobic and hydrophilic materials determines not only the contact angle contrast but also durability, comfort, and compatibility with filtration requirements.

Are Fluoropolymer-Cellulose Systems Optimal for Balance?
Combinations of fluorinated polymers (PTFE, PVDF) with modified cellulose derivatives offer excellent performance balance: fluoropolymers provide exceptional hydrophobicity (contact angles 150-165°) and chemical resistance, while modified cellulose offers natural hydrophilicity, biocompatibility, and comfort. According to research from Nature Communications, fluoropolymer-cellulose Janus membranes can achieve moisture management indices 5-8 times higher than conventional membranes while maintaining 99%+ filtration efficiency for particulate matter. Our preferred combination uses electrospun PVDF nanofibers on the outer surface with plasma-treated cellulose nanofibers on the inner surface, creating membranes that maintain performance through 50+ washing cycles.
What Role Do Nanocomposite Coatings Play?
Nanoparticle coatings can enhance Janus properties without compromising base membrane structure. Hydrophobic enhancement often uses silica nanoparticles with fluorosilane coatings, while hydrophilic enhancement employs titanium dioxide or zinc oxide nanoparticles with hydrophilic surface modifications. Research in Advanced Functional Materials demonstrates that properly applied nanocomposite coatings can increase contact angle contrast by 20-40° while adding minimal weight (typically 1-3% by mass). Our coating approach uses layer-by-layer assembly of oppositely charged nanoparticles, creating gradual property transitions that reduce interfacial stress and improve durability compared to abrupt property changes.
What Performance Metrics Define Superior Janus Membranes?
Understanding key performance indicators helps evaluate different Janus membrane technologies and their suitability for specific applications.

How Is Directional Transport Efficiency Quantified?
The primary metric for Janus membranes is the directional moisture transport capability, typically measured as the difference between moisture vapor transmission rates (MVTR) from hydrophilic to hydrophobic direction versus the reverse direction. High-performance membranes exhibit forward/backward MVTR ratios of 5:1 to 10:1, meaning moisture moves away from the wearer 5-10 times faster than it would move inward. Testing should follow AATCC Test Method 195 for liquid moisture management properties. Our validation shows that optimized Janus membranes achieve MVTR of 1200-1500 g/m²/day in the outward direction versus 200-300 g/m²/day inward, creating effective one-way moisture transport that keeps the wearer significantly drier.
What Filtration Efficiency Can Be Maintained?
While managing moisture, Janus membranes must maintain filtration performance. The best designs achieve PM2.5 filtration efficiency of 95-99% while providing directional moisture transport. Critical factors include: pore size distribution control (typically 0.5-5 μm for effective filtration while allowing vapor passage), fiber diameter consistency, and structural integrity during moisture transport. Testing according to NIOSH standards for particulate filtration confirms that properly engineered Janus membranes can maintain 98%+ filtration efficiency for 0.3 μm particles while achieving superior moisture management compared to conventional filter media.
What Integration Methods Maintain Functionality in Masks?
Successfully incorporating Janus membranes into mask designs requires preserving their asymmetric functionality while ensuring comfort, durability, and manufacturability.

How Does Membrane Orientation Impact Performance?
Correct orientation is absolutely critical—the hydrophobic surface must face outward to repel external liquids, while the hydrophilic surface must face inward to wick moisture away from the skin. Manufacturing processes must ensure 100% orientation accuracy, typically through visual markers, asymmetric edge treatments, or automated optical inspection systems. According to quality control guidelines from ISO 13485 for medical devices, orientation verification should occur at multiple production stages with statistical process control. Our manufacturing uses color-coded backing papers and automated vision systems that verify orientation before cutting and assembly, achieving 99.9%+ orientation accuracy in production.
What Sealing Methods Preserve Directional Properties?
Edge sealing must prevent liquid bypass around the membrane edges while maintaining breathability in the central areas. Common approaches include: ultrasonic welding that creates porous seals, laser cutting that seals edges through localized melting, and frame-based sealing with breathable adhesives. Research from the Textile Institute's technical papers indicates that properly designed edge seals can maintain 95%+ of the membrane's directional transport properties while preventing edge wicking. Our preferred method uses graduated ultrasonic welding that creates stronger seals at potential leak points (bottom edges) and lighter seals elsewhere, optimizing both sealing integrity and overall breathability.
What Durability Challenges Must Be Addressed?
Janus membranes face unique durability challenges due to their asymmetric structure and property gradients, requiring specialized approaches to ensure adequate service life.

How Many Washing Cycles Can Janus Membranes Withstand?
Durability against laundering is crucial for reusable mask applications. High-performance Janus membranes should maintain 80%+ of their original directional transport capability after 20-50 washing cycles depending on construction and materials. Key factors affecting wash durability include: interfacial bond strength between layers, chemical resistance of surface treatments, and structural integrity during mechanical agitation. Testing following AATCC laundering standards demonstrates that membranes with covalent bonds between layers (rather than physical adhesion) typically survive 2-3 times more washing cycles. Our accelerated washing tests show that membranes with plasma-induced crosslinking maintain 85% performance after 30 washing cycles, meeting requirements for most reusable mask applications.
What Is the Impact of Mechanical Flexing and Abrasion?
Mask membranes experience significant flexing during wear and potential abrasion from facial movements. Janus structures are particularly vulnerable at the interface between hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions. Advanced designs use: gradient transitions rather than abrupt interfaces, interfacial reinforcement with nanofibers, and sacrificial protective layers in high-wear areas. Research in Wear journal indicates that Janus membranes with interfacial nanocomposite reinforcements can withstand 10,000+ flex cycles with less than 20% performance degradation. Our flex testing simulates facial movements during speech and expression, with optimized membranes maintaining 90%+ directional transport after equivalent to 100 hours of wear.
Conclusion
Hydrophobic/hydrophilic Janus membranes represent a transformative advancement in intelligent filtration materials, offering unprecedented moisture management capabilities that significantly enhance mask comfort and performance. The best implementations combine sophisticated material engineering with practical manufacturing integration, creating products that actively manage moisture transport rather than merely resisting it. As fabrication methods advance and material costs decrease, Janus membrane technology is poised to move from premium applications to mainstream adoption, fundamentally improving the user experience of respiratory protection across medical, industrial, and consumer applications.
Ready to explore Janus membrane technology for your mask products? Contact our Business Director, Elaine, at elaine@fumaoclothing.com to discuss how directional moisture management can differentiate your products and significantly improve wearer comfort. Our materials engineering team specializes in integrating advanced membrane technologies into practical, manufacturable mask designs.


























