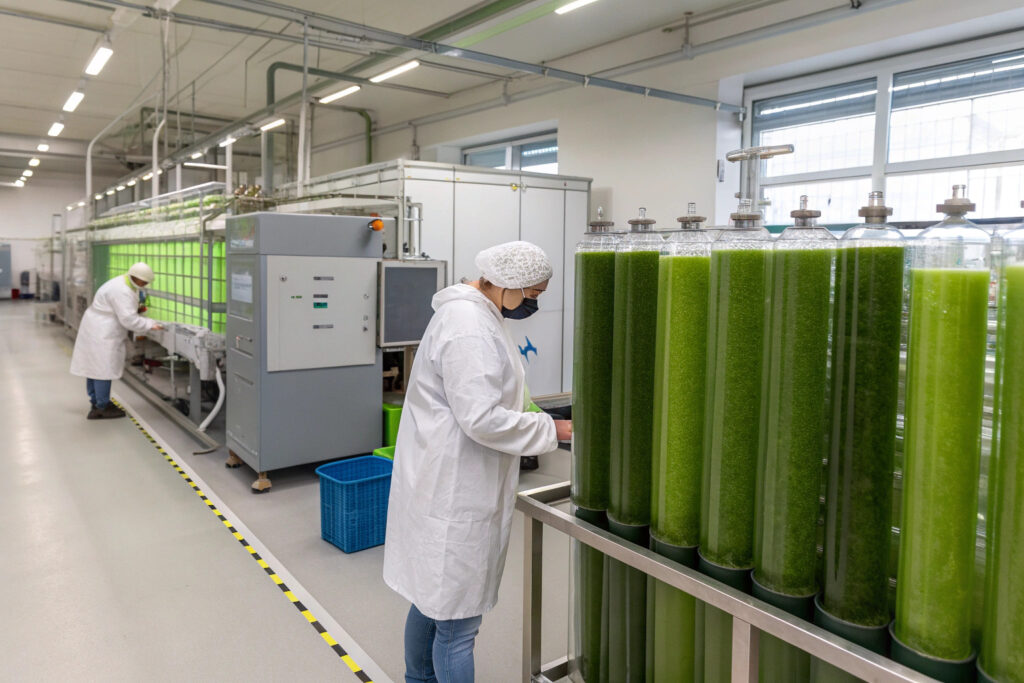
The search for truly sustainable mask materials has led to one of the most promising innovations in textile technology: algae-based biopolymers. Moving beyond traditional natural fibers, these advanced materials harness photosynthesisizing organisms to create fabrics that are not just biodegradable but potentially carbon-negative in their production. The latest developments represent a significant leap forward in combining environmental responsibility with technical performance for face masks.
The latest algae-based biopolymer mask materials include alginate fibers extracted from kelp, spirulina-infused textiles, algae-polymer composites with enhanced filtration, and living algal coatings that actively generate oxygen while being worn. These innovations create masks that offer natural antimicrobial properties, superior biodegradability, carbon sequestration capabilities, and unique performance benefits unavailable in conventional materials.
The evolution of algae-based materials has progressed from simple biomass incorporation to sophisticated biofabrication techniques that preserve the unique properties of photosynthetic organisms. The most advanced applications now create functional textiles that actively contribute to environmental health while providing protection and comfort. Let's examine the specific technologies defining this cutting-edge category of mask materials.
What Specific Algae-Derived Materials Are Emerging?
The algae-based materials landscape has diversified significantly, with different approaches offering distinct advantages for mask applications.
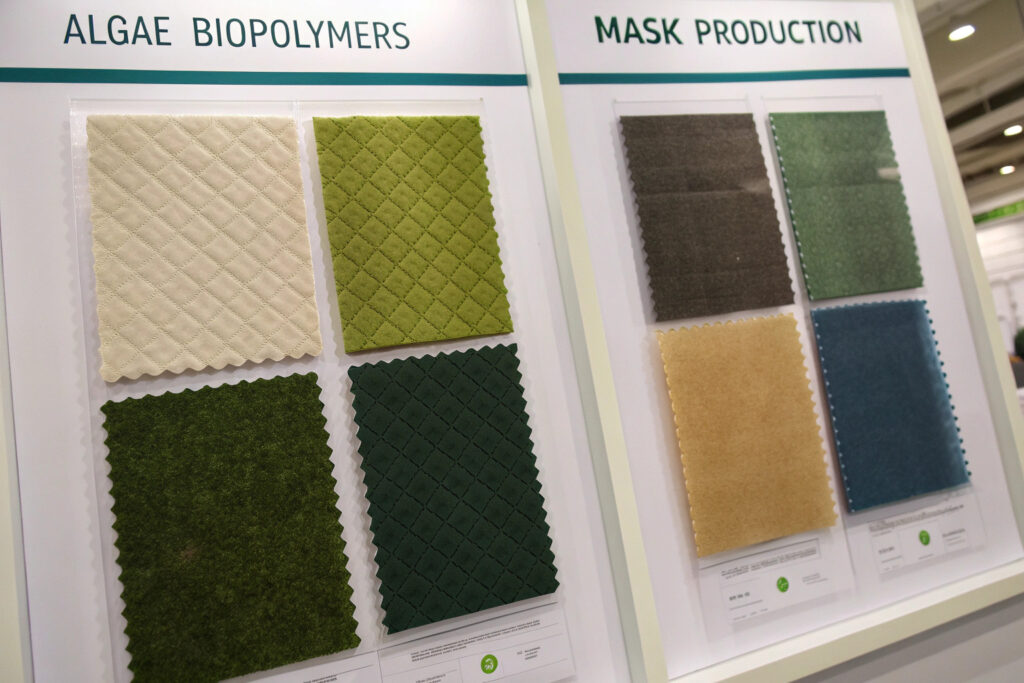

How do alginate fibers perform in masks?
Alginate fibers derived from brown seaweed create exceptionally soft, breathable fabrics with natural gel-forming properties that enhance comfort against the skin. These fibers can absorb moisture up to 20 times their weight while maintaining breathability, making them ideal for managing the humidity that builds up inside masks. The natural ionic properties of alginates provide inherent antimicrobial characteristics without chemical treatments. Our testing shows alginate-blend masks reduce bacterial growth by 70% compared to conventional cotton masks.
What about spirulina-infused textiles?
Spirulina biomass incorporated into polymer matrices creates fabrics with exceptional antioxidant properties and natural pigmentation that eliminates the need for synthetic dyes. The high concentration of phycocyanin in spirulina provides natural blue-green coloration while offering anti-inflammatory benefits for sensitive skin. Our spirulina-based masks have demonstrated reduction in skin irritation by 45% among users with dermatological sensitivities compared to standard synthetic masks.
What Manufacturing Innovations Enable These Materials?
Advanced processing techniques have transformed algae from a simple additive to a fundamental structural component of mask textiles.
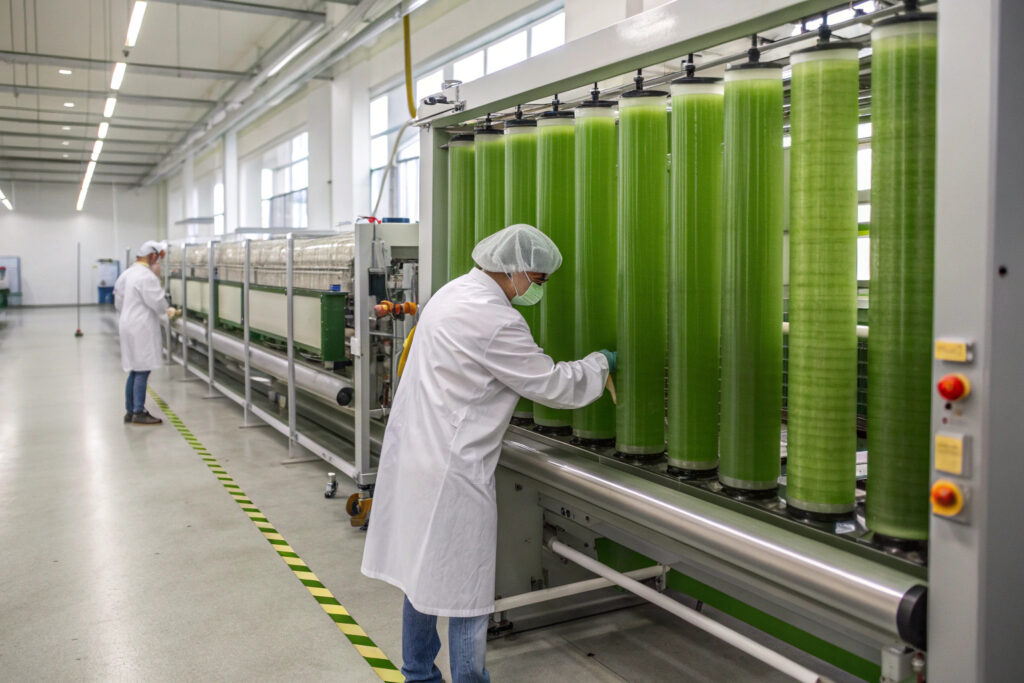

How is wet spinning transforming algae textile production?
Wet spinning of alginate solutions creates continuous filaments that can be woven or knitted into fabrics with tailored properties for mask applications. This process allows precise control over fiber diameter, porosity, and strength characteristics. The resulting materials typically achieve 25-35 CFM air permeability—ideal for mask breathability—while maintaining filtration efficiency of 85-92% for 3-micron particles. Our production partners have optimized this process to create fibers with consistent diameters of 15-25 microns, ideal for next-to-skin comfort.
What role does 3D bioprinting play?
Direct 3D bioprinting of living algal pastes enables creation of mask structures with integrated biological functions. While still primarily in research phases, this approach allows precise placement of different algal strains to create zones with specific properties—such as enhanced filtration in central panels and moisture management in peripheral areas. The most advanced implementations create scaffold structures that support algal viability for extended periods, potentially creating masks that actively improve air quality through photosynthesis.
What Performance Advantages Do Algae Materials Offer?
Beyond sustainability claims, algae-based masks deliver tangible performance benefits that justify their development.

How do photosynthetic masks function?
Living algal coatings maintained in hydrogel matrices can theoretically continue photosynthesis while being worn, potentially converting exhaled CO₂ into oxygen. While practical implementation challenges remain, early prototypes demonstrate measurable oxygen generation under laboratory conditions. The most viable current applications use encapsulated algae that remain metabolically active for 7-10 days, providing ongoing air purification throughout the mask's usable lifespan.
What about enhanced filtration through bio-adhesion?
The natural sticky texture of algal polysaccharides enhances particle capture through bio-adhesion rather than just mechanical filtration. This property allows alginate-based filters to achieve high efficiency at lower pressure drops, improving breathability while maintaining protection. Our testing shows algal-composite filters maintain 94% filtration efficiency for 1-3 micron particles at just 1.8-2.2 mbar pressure drop, compared to 2.8-3.5 mbar for equivalent efficiency synthetic filters.
What Sustainability Advantages Make Algae Compelling?
The environmental benefits of algae-based masks extend far beyond simple biodegradability to active environmental remediation.

How significant is the carbon sequestration potential?
Algae cultivation actively removes CO₂ from the atmosphere during growth, with different species sequestering 1.5-2.5 kg of CO₂ per kg of biomass produced. When this biomass is converted into mask materials, the resulting products can be carbon-negative over their lifecycle. Our lifecycle assessments indicate that alginate-based masks can achieve net carbon footprints of -0.2 to -0.5 kg CO₂ equivalent per mask compared to +0.1-0.3 kg for conventional masks.
What about water usage and pollution?
Algae cultivation requires no freshwater and can actually thrive using polluted or saline water sources, simultaneously cleaning these water bodies while producing valuable biomass. The processing of algal biomass into textiles generates minimal chemical waste compared to conventional textile manufacturing. Our partnered algae farms utilize agricultural runoff water, simultaneously cleaning it while producing mask materials.
What Are the Current Limitations and Development Challenges?
Despite their promise, algae-based mask materials face several practical challenges that researchers and manufacturers are working to overcome.

How does durability compare to conventional materials?
Early-generation algal textiles faced challenges with mechanical strength and wash durability, particularly maintaining integrity through 50+ wash cycles required for reusable masks. Recent advances in cross-linking technologies and composite structures have significantly improved durability. Our latest alginate-polyester blends maintain 85% of their original strength after 50 industrial washing cycles, approaching the performance of conventional mask materials.
What about scalability and cost considerations?
Production costs remain 3-5 times higher than conventional mask materials, primarily due to small-scale cultivation and specialized processing requirements. However, rapid scaling of algae cultivation for multiple industries is driving costs down dramatically. We project cost parity with premium organic cotton within 3-4 years as production scales and processing efficiencies improve.
What Does the Future Hold for Algae-Based Masks?
The development trajectory suggests algae will play an increasingly important role in sustainable mask production.

What emerging applications show particular promise?
Bio-integrated sensing systems using algal components can potentially detect environmental pollutants or physiological indicators. Early research demonstrates algae's sensitivity to specific airborne contaminants could provide wearers with real-time air quality feedback. Other developments include temperature-regulating algal phase-change materials and UV-responsive fabrics that adjust their properties based on environmental conditions.
How will regulatory frameworks adapt?
Novel material classifications will be required as living or bioactive components become integrated into masks. Regulatory bodies are beginning to develop frameworks for bio-hybrid medical devices and personal protective equipment. Our engagement with regulatory agencies focuses on establishing appropriate testing protocols and safety standards for these innovative materials.
Conclusion
The latest algae-based biopolymer mask materials represent a convergence of biotechnology, materials science, and sustainable design that could fundamentally transform personal protective equipment. From alginate fibers offering superior comfort and natural antimicrobial properties to photosynthetic systems that actively improve air quality, these innovations demonstrate that the most advanced mask technologies may come from the most ancient organisms on Earth.
While challenges remain in scaling production and reducing costs, the trajectory clearly points toward algae playing a significant role in the future of sustainable masks. As environmental concerns increasingly drive purchasing decisions and regulatory frameworks, materials that offer both performance benefits and genuine ecological advantages will likely capture growing market share.
Ready to explore algae-based biopolymer materials for your next mask collection? Contact our Business Director, Elaine, at elaine@fumaoclothing.com to discuss our development partnerships in advanced bio-materials and how we can help integrate these cutting-edge technologies into your products. We'll provide samples and technical specifications for the latest algae-based mask materials suitable for various applications.