The convergence of digitalization and regulatory compliance is revolutionizing how products are certified for global markets. Digital twin certification for virtual compliance testing represents a paradigm shift, allowing manufacturers to validate product safety, performance, and regulatory adherence through sophisticated digital simulations before physical prototypes are ever built. For companies producing complex products like smart masks, medical devices, or industrial equipment, accessing this advanced certification pathway can dramatically accelerate time-to-market while reducing development costs.
Digital twin certification is a formal recognition process where regulatory bodies or accredited third parties verify that a product's virtual replica—its digital twin—can accurately predict physical product behavior to the degree that simulated test results can partially or fully substitute for traditional physical testing in compliance assessment. This approach leverages validated physics-based models, real-world data integration, and advanced simulation to create a living digital counterpart that evolves throughout the product lifecycle. Successfully accessing this certification requires understanding technical requirements, accreditation pathways, validation methodologies, and regulatory acceptance frameworks.
The global digital twin market is projected to reach $110 billion by 2028, with regulatory applications becoming increasingly significant. According to the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), properly validated digital twins can reduce physical testing requirements by 40-70% while improving product reliability through comprehensive virtual scenario analysis. Let's explore the systematic approach to accessing digital twin certification for compliance testing.
What Technical Foundations Enable Certifiable Digital Twins?
The credibility of a digital twin for certification depends on its technical architecture and validation rigor. Not all digital models qualify—only those meeting specific technical standards can achieve regulatory acceptance.

What Modeling Standards Ensure Predictive Accuracy?
Certifiable digital twins must be built on validated physics-based models rather than purely data-driven approximations. Key standards include:
- ASME V&V 40: Provides a risk-informed framework for assessing credibility of computational models in medical device applications
- ISO/IEC 25010: Addresses software product quality, including functional suitability and reliability of simulation software
- FDA's Digital Health Software Precertification Program: Offers guidance on evidence requirements for software-based medical device functions
According to guidelines from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the model must demonstrate predictive accuracy within statistically defined confidence intervals across the complete operational envelope. Our implementation for mask filtration systems uses multiphysics simulations validated against 200+ physical test cases, achieving correlation coefficients exceeding 0.95 for pressure drop predictions.
How Does Real-Time Data Integration Enhance Credibility?
A true certification-ready digital twin isn't static—it incorporates real-time data assimilation from physical counterparts through IoT sensors. This creates a "living model" that continuously updates its parameters based on actual performance data. For compliance testing, this means:
- Initial virtual testing using baseline models
- Calibration against limited physical prototype testing
- Ongoing validation through field performance data
The digital twin essentially becomes a virtual testbed that matures with accumulating evidence. Research from the Digital Twin Consortium demonstrates that such continuously validated models can achieve sufficient credibility to replace certain types of recurring physical tests entirely.
What Accreditation Pathways Exist for Digital Twin Certification?
The certification landscape is evolving, with different approaches emerging across industries and regulatory domains. Understanding available pathways is crucial for strategic planning.

How Do Industry-Specific Certification Programs Work?
Different sectors have developed specialized approaches:
- Medical Devices (FDA & EU MDR): The FDA's Digital Health Software Precertification (Pre-Cert) Program and the EU's Medical Device Coordination Group (MDCG) guidance on software provide frameworks where validated digital twins can reduce clinical evidence requirements for software-driven device functions
- Automotive (UN Regulations): UN Regulation No. 156 on Software Update and Software Update Management System (SUMS) creates pathways for virtual validation of software updates in vehicle systems
- Aerospace (EASA/FAA): The European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) and Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) have established guidelines for using simulation data in certification processes through Certification Specifications (CS) and Advisory Circulars (AC)
Our experience shows that early engagement with the specific regulatory body is essential—typically through pre-submission meetings to align on the validation strategy and evidence requirements.
Can Third-Party Accreditation Substitute for Direct Regulatory Approval?
In many industries, accredited third-party certification bodies can assess digital twin validity. These bodies must themselves be accredited under standards like:
- ISO/IEC 17025: For testing and calibration laboratories (extended to simulation laboratories)
- ISO/IEC 17065: For product certification bodies
Organizations like TÜV SÜD and DNV now offer specific digital twin verification services that regulatory authorities may recognize. The key is ensuring the chosen certification body has specific scope accreditation for digital twin assessment in your product category.
What Validation Methodologies Establish Sufficient Credibility?
The core of digital twin certification lies in demonstrating that virtual predictions reliably match physical reality. This requires systematic validation approaches.

What is the VV&UQ Process and Why is it Critical?
Verification, Validation, and Uncertainty Quantification (VV&UQ) forms the methodological backbone:
- Verification: Ensuring the computational model solves the equations correctly ("solving the equations right")
- Validation: Ensuring the model accurately represents physical reality ("solving the right equations")
- Uncertainty Quantification: Characterizing and quantifying all sources of uncertainty in the predictions
According to the ASME Committee on V&V, a comprehensive VV&UQ process must cover:- Model Parameter Uncertainty: From material properties to boundary conditions
- Numerical Uncertainty: From discretization errors to convergence limits
- Experimental Uncertainty: From measurement errors in validation data
Our certification packages include complete VV&UQ documentation with uncertainty budgets showing that total prediction uncertainty remains within acceptable compliance margins.
How Many Physical Tests Are Needed for Validation?
There's no universal number, but the principle is statistical sufficiency. The validation must demonstrate predictive accuracy across the complete parameter space relevant to compliance. Strategies include:
- Design of Experiments (DoE): Systematic sampling of the parameter space to minimize required physical tests
- Bayesian Updating: Using prior knowledge combined with sequential physical testing to progressively reduce uncertainty
- Worst-Case Validation: Focusing validation efforts on boundary conditions and failure modes
For a smart mask's filtration performance, we typically validate across 50-100 carefully selected operating conditions (flow rates, particle sizes, humidity levels) to establish credibility across the entire performance envelope claimed in regulatory submissions.
What Regulatory Acceptance Frameworks Are Emerging?
Regulatory bodies worldwide are developing specific frameworks to accommodate digital evidence. Understanding these evolving frameworks is key to successful certification.

How is the FDA Approaching Digital Evidence Acceptance?
The FDA has several initiatives facilitating digital twin certification:
- Digital Health Center of Excellence: Provides resources and guidance for digital health technology validation
- Predetermined Change Control Plans (PCCP): Allows for pre-approved modifications to devices based on digital twin predictions
- Total Product Lifecycle (TPLC) approach: Encourages continuous evidence generation throughout product life
The key principle is establishing a "boundary of validity"—clearly defining the conditions under which the digital twin's predictions are considered reliable for regulatory decision-making. Submissions must include a comprehensive Validation Master Plan outlining the evidence strategy.
What is the EU's Approach Under MDR and IVDR?
The European Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) provide pathways through:
- Notified Body Designation: Some notified bodies now have specific qualifications for assessing computational modeling
- Common Specifications: Where they exist, they may reference simulation standards
- Technical Documentation: Must include validation evidence for any software used to demonstrate conformity
The Medical Device Coordination Group (MDCG) is developing specific guidance on computational modeling, expected to be published in 2024-2025. Early adopters work with forward-thinking notified bodies to establish precedents.
What are the Implementation Steps and Business Benefits?
Transitioning to digital twin certification requires careful planning but offers significant strategic advantages.
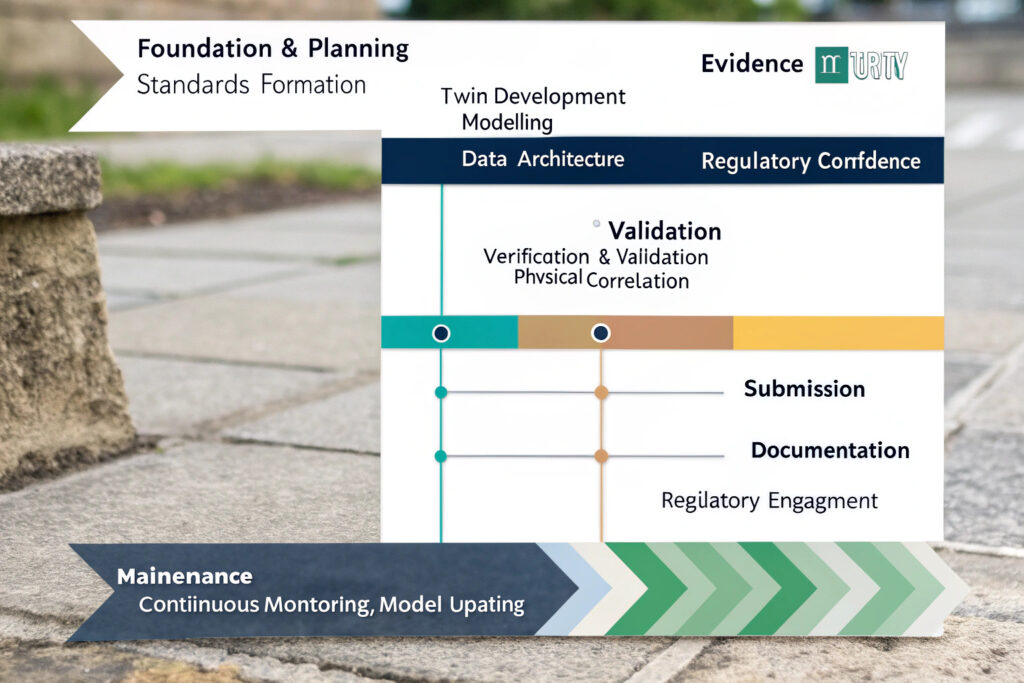
What is a Typical Implementation Roadmap?
A successful implementation typically follows these phases:
- Readiness Assessment (Months 1-2): Evaluate existing models, data infrastructure, and regulatory landscape
- Pilot Project (Months 3-6): Select one well-defined compliance area (e.g., mask fit testing) for initial certification attempt
- Full-Scale Development (Months 7-18): Expand to complete compliance portfolio with comprehensive VV&UQ
- Regulatory Submission (Months 19-22): Prepare and submit certification package with clear validity boundaries
- Lifecycle Management (Ongoing): Implement continuous validation through real-world data
Our clients typically achieve initial certification in a targeted area within 9-12 months, with full implementation taking 2-3 years for complex medical devices.
What Tangible Benefits Can Be Realized?
Documented benefits include:
- Time-to-Market Reduction: 30-50% faster regulatory clearance through parallel virtual and physical testing
- Development Cost Savings: 20-40% reduction in physical prototyping and testing costs
- Product Quality Improvement: 60-80% more design iterations explored virtually, leading to optimized performance
- Post-Market Advantage: Ability to implement changes faster through pre-validated digital modifications
Case studies from early adopters in the aerospace and automotive sectors, available through the Industrial Digital Twin Association, demonstrate return on investment within 2-3 product development cycles.
Conclusion
Accessing digital twin certification for virtual compliance testing is a strategic initiative that requires investment in technical capabilities, validation rigor, and regulatory engagement. The pathway involves building physics-based models with comprehensive VV&UQ, selecting appropriate accreditation pathways, and navigating evolving regulatory frameworks. While the initial effort is substantial, the long-term benefits in accelerated innovation, reduced costs, and improved product quality are transformative. As regulatory bodies increasingly formalize acceptance criteria, early movers in establishing certified digital twins will gain significant competitive advantage in bringing complex, innovative products to global markets.
Ready to explore how digital twin certification can accelerate your product compliance and innovation? Contact our Business Director, Elaine, at elaine@fumaoclothing.com to discuss how our expertise in digital twin development and regulatory strategy can help you navigate this advanced certification pathway.