The proliferation of smart masks with integrated electronics—from sensors and LED lights to active filtration fans—has created a critical need for convenient, durable power solutions. Integrated wireless charging addresses this need by eliminating physical ports, enhancing waterproofing, and improving user experience. For manufacturers and buyers of advanced PPE, understanding how to source masks with this seamless power technology is essential for delivering next-generation products.
Masks with integrated wireless charging incorporate a receiver coil and power management circuitry within the mask structure, allowing them to be powered or recharged by simply placing them on or near a compatible wireless charging transmitter (pad or stand), thereby eliminating the need for exposed USB ports and enabling more robust, sealed designs. This technology is key for creating truly washable, user-friendly smart masks that maintain functionality over time. Successful sourcing requires evaluating charging standards, coil integration methods, power efficiency, and overall system reliability.
The wireless power market is projected to exceed $40 billion by 2028, with wearable applications growing rapidly. The convenience and reliability of cord-free charging are becoming expected features in high-end consumer electronics and medical devices. For smart masks used in healthcare, industrial, or consumer settings, this feature can significantly improve adoption and daily usability. Let's explore the practical considerations for sourcing these advanced products.
What Wireless Charging Standards Are Suitable for Masks?
The choice of wireless charging standard dictates compatibility, charging speed, efficiency, and design constraints. Not all standards are equally suited to the form factor and power needs of a smart mask.

Is the Qi Standard the Best Choice?
Qi (pronounced "chee"), developed by the Wireless Power Consortium (WPC), is the dominant standard for consumer electronics (up to 15W for phones, with a baseline of 5W).
- Advantages for Masks: Ubiquitous compatibility. Users likely already own a Qi charger. The standard is mature, with many certified, low-cost receiver chips and coils available.
- Challenges: Requires relatively close coupling (coils within ~5mm). Precise alignment between the mask's receiver coil and the transmitter pad is needed for good efficiency. This can be tricky with a flexible mask unless a dedicated charging dock or specific placement marker is provided.
- Power Level: Most smart mask electronics (sensors, small fans, LEDs) consume less than 2-3W. The 5W baseline of Qi is more than sufficient, making it a strong, versatile candidate.
Sourcing Qi-certified masks ensures broad interoperability but requires the manufacturer to have designed for the alignment challenge.
What About AirFuel Resonant or Proprietary Solutions?
- AirFuel Resonant: This standard allows for greater spatial freedom (charging over distances of up to several centimeters) and less strict alignment. This could allow a mask to be charged in a bin or on a hook near a transmitter. However, the ecosystem is less mature than Qi, and consumer transmitters are far less common.
- Proprietary Low-Power Systems: Some manufacturers develop their own optimized system for a specific product. This can allow for perfect mechanical integration (e.g., a mask that always sits in a specific dock) and higher efficiency at the target power level. The major drawback is that it requires the user to use the proprietary charger provided, losing universal compatibility.
For most sourcing scenarios aiming for consumer convenience, Qi remains the most practical and future-proof standard, provided the mask design includes a solution for consistent coil placement during charging.
How is the Wireless Charging System Integrated into the Mask?
The physical and electrical integration of the receiver coil and its circuitry is the core engineering challenge that determines the mask's durability, comfort, and charging performance.
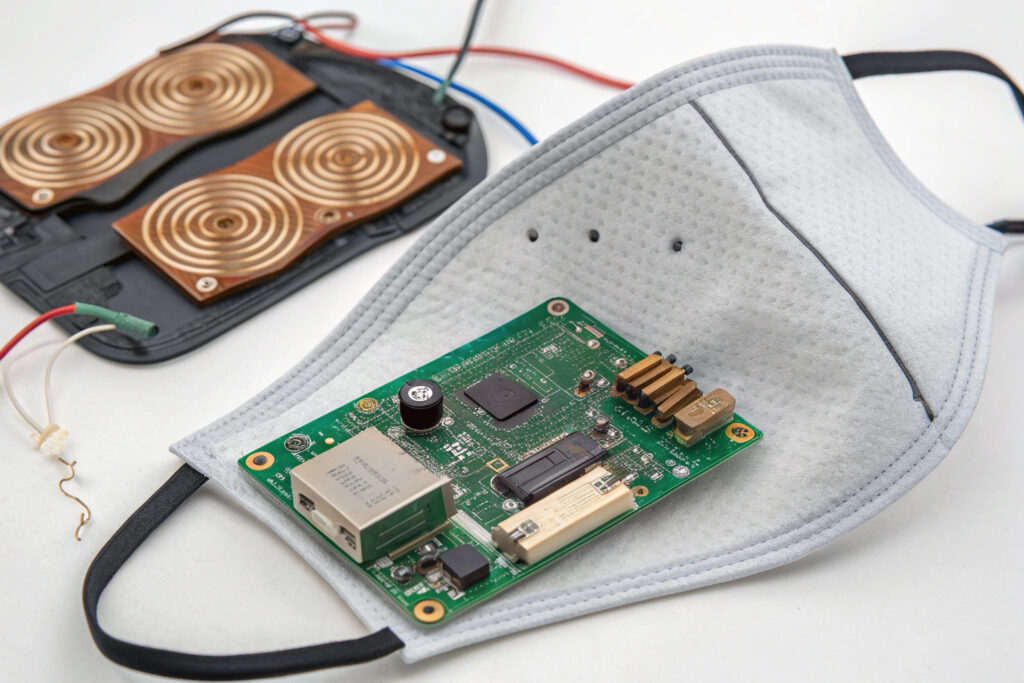
How is the Receiver Coil Designed and Placed?
The receiver coil is a flat spiral of insulated wire (typically Litz wire to reduce AC resistance) or a etched trace on a flexible printed circuit board (FPCB).
- Placement Strategy: The coil must be positioned in a area of the mask that will consistently make contact with or be near the charging pad. Common locations include:
- The Top Edge/Brow Area: If the mask is designed to lay flat on a charging pad.
- A Rigid Module/Cartridge: If the smart components are housed in a removable, rigid front module, the coil can be integrated there for optimal alignment.
- Design for Flexibility: If the mask body is flexible, the coil and its connecting FPCB must be designed to withstand repeated bending without fatigue failure. This often involves using specially designed flexible adhesives and strain relief.
How are Electronics Protected from Moisture and Damage?
A major advantage of wireless charging is the ability to fully seal the device. This requires:
- Potting or Encapsulation: The receiver coil, power management IC, and associated components are typically encapsulated in a waterproof resin (potting compound) within a rigid or semi-rigid module, or between laminated fabric layers.
- Absence of Ports: The complete elimination of any USB or DC jack removes a primary point of failure for water and dust ingress (IP rating improvement).
- Battery Integration: The lithium-polymer battery must also be securely connected and sealed within the assembly. Wireless charging facilitates easier sealing compared to a port-based design.
When sourcing, inquire about the Ingress Protection (IP) rating (e.g., IP67) and the specific methods used for waterproofing the electronics.
What Are the Key Performance and Safety Considerations?
Beyond simply charging, the system must be efficient, safe, and reliable over the product's lifetime.

How is Charging Efficiency and Thermal Management Handled?
- Efficiency: The end-to-end efficiency (wall power to battery power) of a wireless charging system is lower than wired charging due to coupling and conversion losses. For a low-power device like a mask, this is less critical but still impacts charging time and energy waste. Look for systems that maintain a reasonable efficiency (e.g., 60-75% at the expected operating point).
- Heat Generation: Inefficiencies manifest as heat, generated in both the transmitter pad and the receiver coil in the mask. Proper design minimizes this through coil optimization and circuit design. The mask must not become uncomfortably warm during charging, especially if it's being charged while stored in a confined space. Thermal cutoffs and monitoring in the power management IC are essential for safety.
What Safety and Regulatory Certifications are Needed?
A wireless charging system is both an electronic device and a means of charging a lithium-ion battery. Key certifications include:
- Qi Certification: If using the Qi standard, the receiver must be certified by the WPC to ensure interoperability and safety compliance with the standard's protocols (e.g., foreign object detection).
- Electrical Safety: Compliance with standards like IEC 62368-1 (Audio/Video, Information and Communication Technology Equipment).
- Battery Safety: The battery and its charging circuit should be designed and tested per relevant standards (like UL 2054 or IEC 62133).
- EMC/Radio: The wireless power transfer system must not cause harmful interference and must be immune to it, requiring FCC/CE-EMC compliance.
Sourcing from manufacturers who can provide these certifications significantly reduces risk and ensures market access.
What Are the Primary User Experience and Application Benefits?
The value of integrated wireless charging extends beyond the technical specifications to tangible benefits in how the mask is used and maintained.
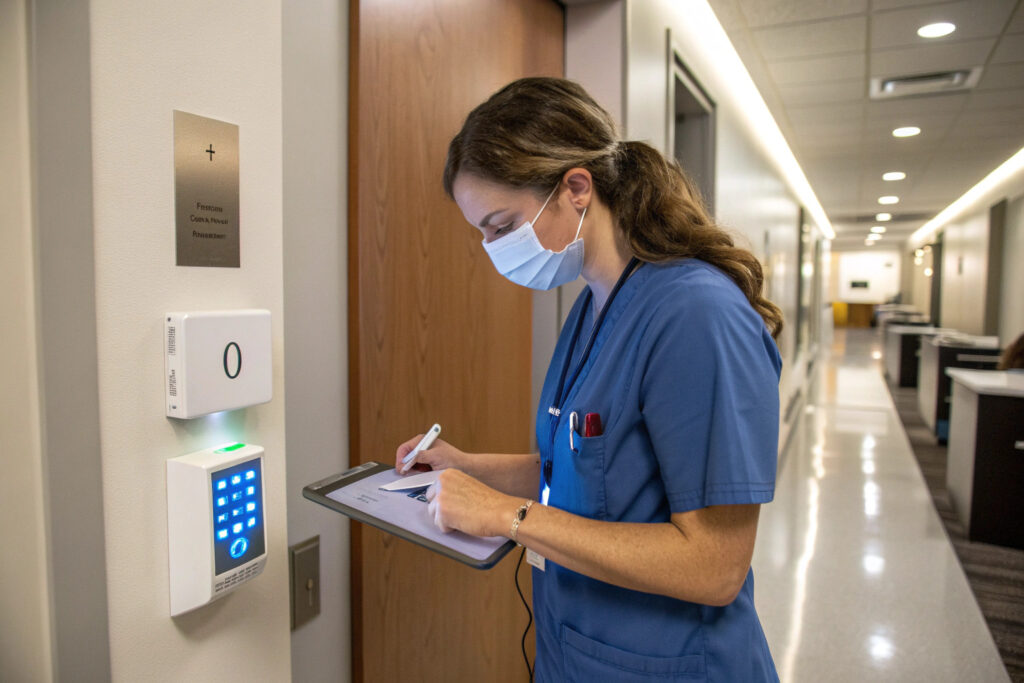

How Does It Enhance Usability in Professional Settings?
In environments like hospitals, laboratories, or cleanrooms:
- Hygiene and Durability: No ports means fewer crevices for pathogens or contaminants to collect. The mask can be more easily wiped down or subjected to UV disinfection without worrying about damaging a charging port.
- Streamlined Workflow: Charging pads can be installed at workstations, allowing staff to conveniently recharge masks between uses without managing individual cables. This ensures devices are always ready.
- Reduced Wear and Tear: Physical charging ports are a common point of mechanical failure. Removing them increases the product's overall ruggedness and lifespan.
What is the Appeal for Consumer Smart Masks?
For everyday users:
- Convenience: Aligns with the "drop and charge" habit established by smartphones, smartwatches, and earbuds.
- Aesthetic and Design Freedom: Allows for cleaner, unbroken design lines without port cutouts.
- Water Resistance: Supports claims of washability or sweat resistance, which is a key consumer demand for reusable masks.
When sourcing, consider if the manufacturer provides an accompanying charging pad or dock, or if the mask is compatible with widely available third-party Qi chargers.
Conclusion
Sourcing masks with integrated wireless charging requires a focus on selecting the right standard (with Qi being the most universally practical), verifying the robustness of the coil and electronics integration (especially for waterproofing), and confirming the necessary safety and performance certifications. The best implementations will offer a seamless, reliable charging experience that feels intuitive to the user, whether in a hectic hospital or at home. This feature is no longer just a luxury; for smart masks designed for daily, reliable use, it is becoming a critical enabler of durability, hygiene, and user satisfaction.
Ready to source smart masks with the convenience and reliability of integrated wireless charging? Contact our Business Director, Elaine, at elaine@fumaoclothing.com to discuss available models, custom integration options, and how this feature can elevate your smart PPE offerings.