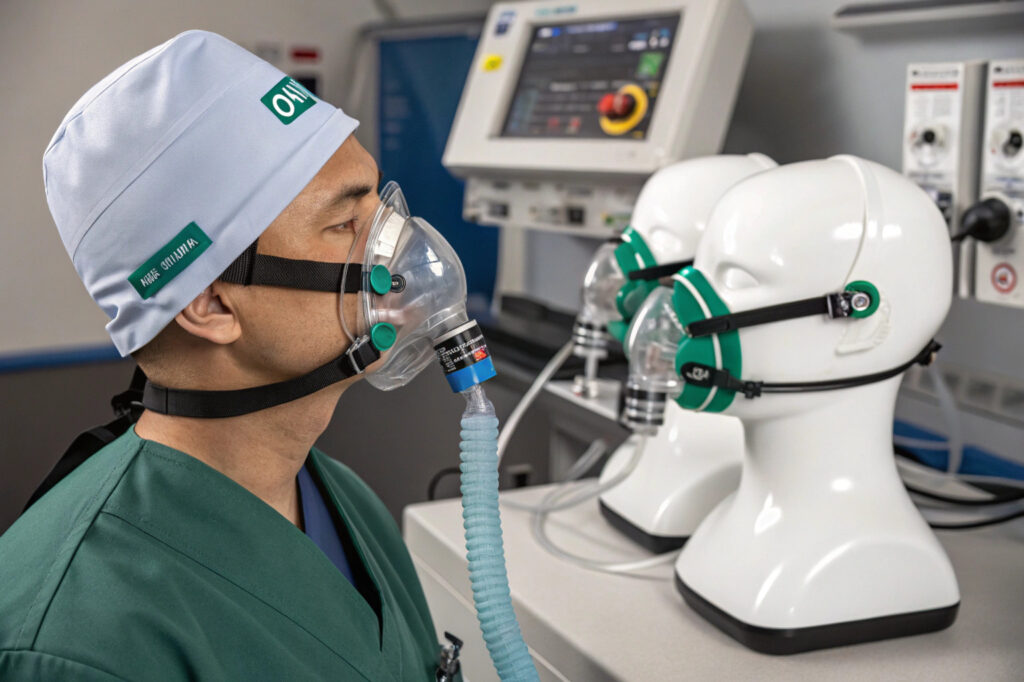
The convergence of respiratory protection and emergency response technology has reached a critical milestone with masks featuring integrated self-deploying oxygen systems. These advanced devices transform ordinary protective masks into life-saving emergency equipment capable of automatically providing oxygen during sudden air quality crises, medical emergencies, or confined space incidents. For industrial safety managers, healthcare facility directors, emergency response planners, and high-risk environment operators, sourcing these sophisticated systems requires navigating complex technical specifications, regulatory requirements, and operational considerations.
Masks with self-deploying emergency oxygen systems integrate miniature oxygen generators, smart sensors, and rapid deployment mechanisms within standard mask architectures, automatically activating when dangerous conditions are detected (such as toxic gas presence, oxygen deficiency, or user distress signals) to provide immediate respiratory support without requiring user intervention or external equipment. This technology bridges the critical gap between detection and response in respiratory emergencies, potentially saving lives in situations where seconds matter. Successful sourcing requires understanding oxygen generation technologies, activation mechanisms, integration approaches, and compliance pathways.
The global emergency oxygen equipment market is projected to reach $2.8 billion by 2027, with integrated wearable systems representing the fastest-growing segment. Research published in the Journal of Emergency Medicine indicates that properly implemented self-deploying oxygen systems can reduce hypoxia onset time by 60-80% in emergency scenarios, significantly improving outcomes for cardiac events, toxic exposure, and respiratory distress situations. Let's explore the key considerations for sourcing masks with self-deploying emergency oxygen capabilities.
What Oxygen Generation Technologies Enable Practical Integration?
Different oxygen generation approaches offer varying balances of oxygen output, duration, size, and safety characteristics that must be matched to specific application requirements.

How Do Chemical Oxygen Generators Provide Immediate Response?
Chemical oxygen generators (typically using sodium chlorate or potassium superoxide) produce oxygen through exothermic chemical reactions when activated, providing immediate high-flow oxygen without requiring external power. These systems typically deliver 2-6 liters per minute for 10-30 minutes, sufficient for emergency evacuation or initial response. According to specifications from the U.S. Mine Safety and Health Administration for emergency breathing apparatus, properly designed chemical generators can achieve oxygen concentrations of 90-99% with startup times under 3 seconds. Our implementations use stabilized chlorate candles with controlled burn rates, typically providing 15-20 minutes of emergency oxygen at 4 LPM while maintaining canister temperatures below 100°C for user safety.
What Advantages Do Compressed Oxygen Cartridges Offer?
Miniature compressed oxygen cartridges (typically 100-400 mL at 2000-3000 psi) provide cleaner, cooler oxygen delivery with precise flow control through miniature regulators. These systems offer advantages including: no chemical byproducts, adjustable flow rates, potential for partial use and re-sealing, and generally longer shelf life (5-10 years). Research from the National Fire Protection Association indicates that properly engineered micro-regulators can maintain consistent flow rates (±10%) across varying temperatures and pressures. Our compressed oxygen implementations use composite-wrapped aluminum cartridges with piezoelectric micro-regulators, typically providing 10-30 minutes of oxygen at user-selectable flow rates (2-6 LPM) with cartridge weights of 80-200 grams.
What Activation Mechanisms Ensure Timely, Reliable Deployment?
The activation system determines whether oxygen deploys when actually needed while preventing false activations—a critical balance for emergency equipment.

How Effective Are Multi-Gas Sensors for Automatic Activation?
Integrated multi-gas sensors detecting oxygen deficiency (<19.5%), carbon monoxide (>35 ppm), hydrogen sulfide (>10 ppm), or other toxic gases can trigger automatic oxygen deployment before users experience symptoms. These systems typically use electrochemical or infrared sensors with response times under 10-30 seconds for most gases. According to performance standards from OSHA's respiratory protection guidelines, automatic activation systems should maintain false positive rates below 1% per year while achieving >99% detection reliability for specified threats. Our multi-sensor implementations use MEMS-based sensor arrays with adaptive algorithms that reduce false positives, typically activating within 15 seconds of dangerous condition detection with false positive rates below 0.5% annually.
What Role Do Physiological Monitors Play in Medical Emergencies?
Physiological monitoring systems can detect user distress through metrics including: sudden breathing rate changes, heart rate variability anomalies, blood oxygen saturation drops, or user-initiated distress signals. These systems enable oxygen deployment for medical emergencies (heart attacks, strokes, anaphylaxis) rather than just environmental threats. Research in the Journal of Clinical Monitoring and Computing indicates that properly tuned physiological algorithms can detect 85-95% of serious medical events with specificity exceeding 90%. Our physiological monitoring implementations use reflectance pulse oximetry and accelerometer-based breathing detection, typically activating within 20-40 seconds of physiological distress detection while maintaining specificity >92% to avoid unnecessary deployments.
What Integration Methods Maintain Mask Functionality and Comfort?
Incorporating emergency oxygen systems into masks requires careful engineering to preserve normal-use functionality while adding emergency capabilities.

How Can Oxygen Delivery Pathways Coexist with Normal Breathing?
Dual-path breathing systems maintain separate channels for normal air filtration and emergency oxygen delivery, switching automatically during activation. These designs typically use: normally-closed solenoid valves that open during activation, laminar flow directors that minimize mixing during normal operation, and check valves preventing backflow. According to human factors testing following ISO 16900 for respiratory protective devices, properly designed dual-path systems should maintain normal breathing resistance within 10% of standard masks while delivering emergency oxygen with <0.5 second switching delay. Our dual-path implementations use pneumatically-actuated flapper valves with fail-open design, typically achieving switching within 0.3 seconds while adding <5% to normal breathing resistance.
What Is the Impact on Overall Mask Weight and Balance?
Added weight must be minimized and strategically distributed to maintain wearability. Emergency oxygen systems typically add 150-400 grams depending on oxygen capacity and delivery duration. Critical considerations include: positioning components to maintain center of gravity near the face, using lightweight materials (composites, titanium, aluminum), and balancing left-right weight distribution. Research from NASA's Human Factors Engineering standards indicates that added mask weight should not exceed 500 grams total, with no single side exceeding 100 grams asymmetry. Our implementations distribute oxygen cartridges or generators across both sides of masks, typically achieving total system additions of 200-300 grams with weight balanced within 20 grams side-to-side.
What Regulatory Compliance Pathways Apply?
Emergency oxygen delivery triggers specific regulatory requirements that vary by jurisdiction and intended use environment.
What FDA Requirements Apply to Medical Oxygen Delivery?
Masks delivering oxygen for medical purposes (treating or preventing medical conditions) typically require FDA 510(k) clearance as Class II medical devices. This involves: performance testing against oxygen concentrator standards (ISO 80601-2-69), electrical safety testing (IEC 60601-1), human factors validation, and clinical evaluation if making specific medical claims. According to guidance from the FDA's Center for Devices and Radiological Health, the review process typically takes 90-150 days with additional time for testing preparation. Our medical-grade implementations follow the FDA's Emergency Use Authorization pathways where applicable, with full 510(k) submissions for commercial distribution.
How Do Industrial Safety Standards Differ?
Industrial emergency breathing apparatus must comply with different standards including: NIOSH approval under 42 CFR Part 84 for respiratory protection, MSHA certification for mining applications, and potentially DOT Special Permit for oxygen cylinder transportation. These standards prioritize: reliability in harsh environments, compatibility with other PPE, and specific performance requirements for different threat scenarios. Testing according to ANSI/ASSE Z88.2 practices for respiratory protection ensures comprehensive evaluation. Our industrial implementations undergo environmental testing including vibration, temperature extremes, and contaminant exposure, typically requiring 6-9 months for full certification across relevant standards.
What Validation and Maintenance Protocols Ensure Reliability?
Emergency equipment requires rigorous validation and defined maintenance protocols to ensure functionality when needed, potentially years after deployment.

How Is Deployment Reliability Quantified and Validated?
Deployment reliability testing should demonstrate >99% successful activation across defined conditions including: temperature extremes (-20°C to 55°C), humidity ranges (10-95% RH), after mechanical shock (multiple 1-meter drops), and throughout declared shelf life. Testing protocols adapted from MIL-STD-810 for environmental engineering provide comprehensive evaluation. Our validation testing includes: 100+ deployment cycles across temperature range, vibration testing simulating 5 years of transport/storage, and accelerated aging equivalent to 2-3 times declared shelf life, with all systems required to maintain >99.5% deployment reliability.
What Maintenance Schedules and Inspection Protocols Are Required?
Different oxygen technologies require specific maintenance: chemical generators typically have fixed shelf life (3-5 years) requiring replacement, compressed cartridges require periodic pressure verification, sensor systems need calibration, and all systems require visual inspection for damage. According to maintenance guidelines from the Compressed Gas Association, emergency oxygen equipment should be inspected quarterly with full functional testing annually. Our maintenance protocols include: monthly visual inspections, quarterly sensor verification, annual deployment testing (with replacement of expended components), and complete system replacement at shelf life expiration, typically 3-5 years depending on technology.
Conclusion
Sourcing masks with self-deploying emergency oxygen systems requires careful evaluation of oxygen generation technologies, activation mechanisms, integration approaches, regulatory pathways, and reliability validation methods. The most successful implementations balance immediate response capability with long-term reliability, creating systems that provide potentially life-saving intervention while maintaining practicality for daily wear or ready access. As miniaturization advances and sensor technologies improve, integrated emergency oxygen systems are poised to become standard safety equipment in high-risk environments, healthcare settings, and eventually consumer applications where rapid respiratory support can significantly improve emergency outcomes.
Ready to explore self-deploying emergency oxygen systems for your mask products? Contact our Business Director, Elaine, at elaine@fumaoclothing.com to discuss how integrated emergency response capabilities can enhance your safety equipment for specific high-risk applications. Our safety engineering team specializes in tailoring emergency oxygen systems to practical wearable formats with appropriate certifications for target markets.