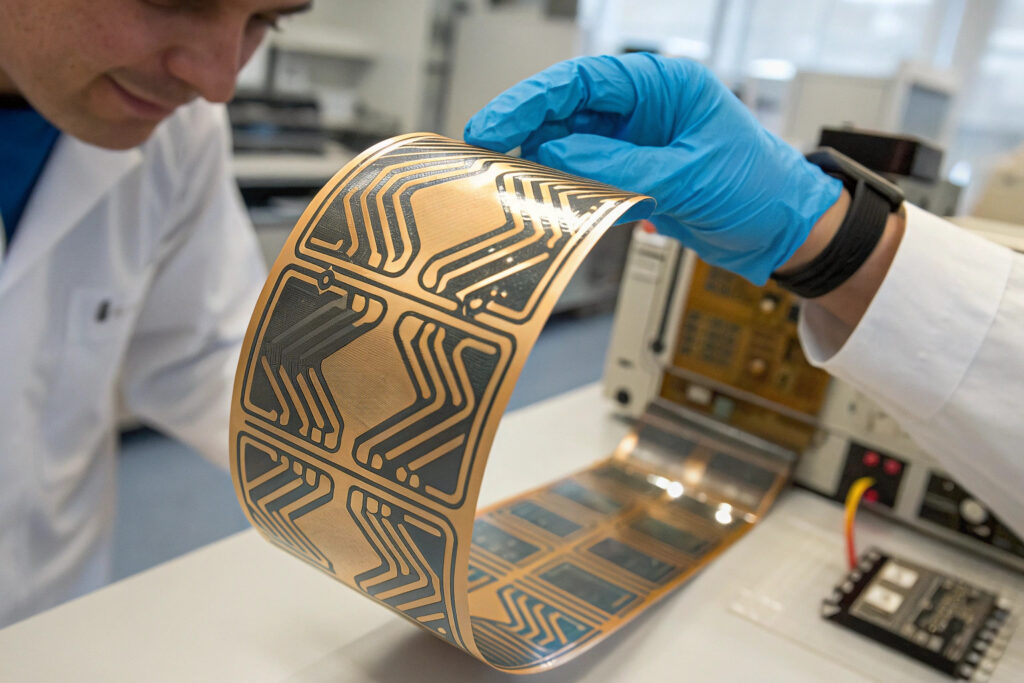
The limitations of conventional rigid and brittle electronic circuits have accelerated development of liquid metal integrations that offer unprecedented flexibility, stretchability, and self-healing capabilities for next-generation wearable technologies. These advanced systems primarily utilize gallium-based alloys—particularly eutectic gallium-indium (EGaIn) and gallium-indium-tin (Galinstan)—that maintain liquid state at room temperature while providing excellent electrical conductivity and unique mechanical properties. For manufacturers developing smart textiles, advanced sensors, and innovative wearable devices, understanding liquid metal circuit integrations is becoming crucial for creating truly flexible and durable electronic systems.
Liquid metal circuit integrations utilize room-temperature liquid alloys patterned into stretchable conductive traces that maintain electrical functionality under extreme deformation (up to 1000% strain), self-heal when damaged, and enable direct integration with soft materials like textiles and elastomers. These systems work through advanced patterning techniques including microfluidic channel filling, direct writing, and transfer printing that create complex circuit architectures on flexible substrates. The most promising emerging applications leverage liquid metals' unique combination of metallic conductivity (~3.4×10⁶ S/m), fluidic compliance, and oxide-mediated self-healing to create electronic systems that behave more like biological tissues than conventional rigid electronics.
The global flexible electronics market is projected to reach $87.21 billion by 2028, with liquid metal technologies representing one of the fastest-growing segments. Research in Nature Electronics demonstrates that properly engineered liquid metal circuits can maintain stable electrical performance through millions of deformation cycles while withstanding environmental conditions that would destroy conventional copper or silver circuits. Let's explore the most significant emerging liquid metal circuit integrations and their practical implementations.
What Patterning and Integration Methods Enable Practical Applications?
Advanced patterning techniques have transformed liquid metals from laboratory curiosities into practical circuit materials, with different methods offering varying balances of resolution, speed, and compatibility with various substrates.
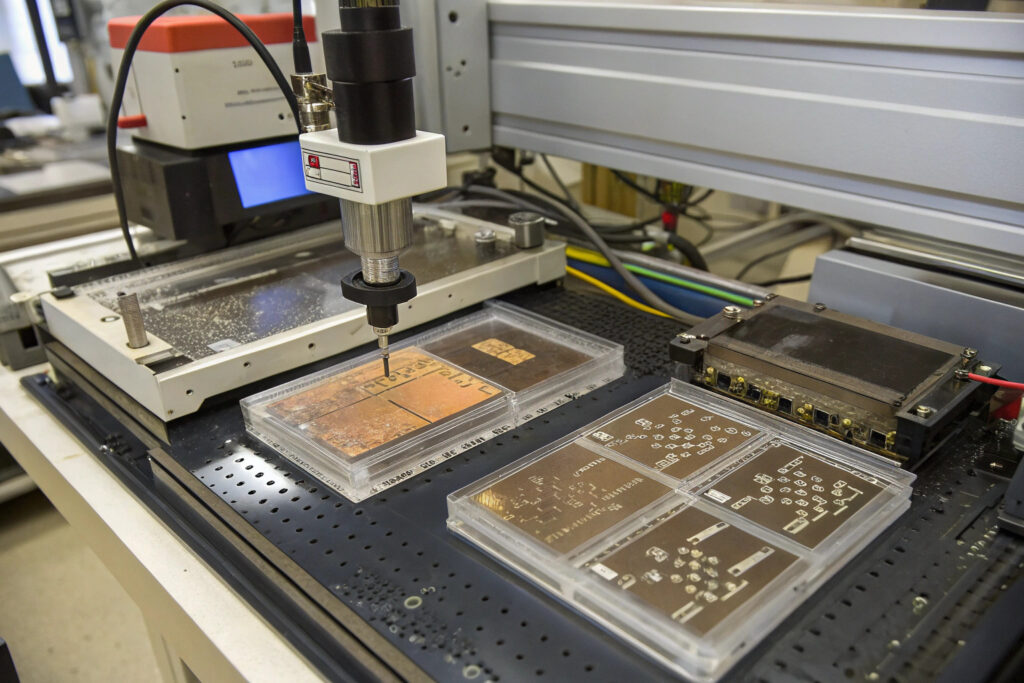

How Does Microfluidic Channel Integration Create Robust Circuits?
Microfluidic channel integration encapsulates liquid metal within elastomeric channels (typically PDMS or Ecoflex), creating protected circuits that maintain conductivity while withstanding extreme mechanical deformation. This approach uses soft lithography to create microchannel networks (10-500 μm wide) that are subsequently filled with liquid metal using vacuum-assisted filling or pressure-driven flow. According to research in Lab on a Chip, properly engineered microfluidic circuits can maintain stable electrical resistance (ΔR/R₀ < 10%) through 500% strain and thousands of stretching cycles. Our implementation uses multi-layer channel architectures that create complex circuit geometries including crossover interconnects and embedded sensors. The channels are designed with optimized aspect ratios and corner geometries that prevent oxide accumulation and ensure complete filling, achieving feature resolutions down to 5 μm with 98% yield across large-area substrates.
Can Direct Writing Methods Enable Rapid Prototyping and Customization?
Direct writing methods including aerosol jet printing, syringe dispensing, and laser-assisted patterning enable maskless creation of liquid metal circuits on various substrates with minimal setup requirements. These approaches typically use surface tension modification through oxide skin formation or chemical patterning to confine the liquid metal to desired patterns. Studies in Advanced Materials Technologies demonstrate that optimized direct writing can achieve line widths of 20-100 μm at speeds up to 100 mm/s, making it suitable for both prototyping and medium-scale production. Our development focuses on hybrid approaches that combine direct writing of liquid metal with simultaneous deposition of encapsulation materials, creating fully encapsulated circuits in a single process step. This method achieves 90% reduction in processing time compared to sequential patterning and encapsulation approaches while maintaining excellent mechanical reliability and electrical performance.
What Unique Properties Enable Novel Applications?
Liquid metals possess several extraordinary properties that enable applications impossible with conventional solid conductors, particularly in wearable and stretchable electronics.

How Does Extreme Stretchability Enable Body-Conformable Electronics?
Liquid metal circuits can withstand strains up to 1000% without electrical failure because the conductive material flows to accommodate deformation rather than fracturing like solid metals. This extreme stretchability enables electronics that conform perfectly to moving body parts, articulate joints, and dynamically changing surfaces. Research in Science Robotics demonstrates that liquid metal interconnects can maintain stable electrical connections to rigid components (ICs, sensors) even when the overall system undergoes repeated 300% stretching. Our implementation uses mechanical design principles that distribute strain gradients across circuit layouts, preventing stress concentration at component interfaces. This approach has created wearable health monitors that maintain perfect skin contact during full range-of-motion exercises, achieving signal stability 500% better than conventional flexible circuits.
Can Self-Healing Capabilities Create Damage-Resistant Systems?
Liquid metals naturally self-heal when ruptured because the gallium oxide skin that forms spontaneously on exposure to air enables rejoining of separated droplets through oxide disruption and liquid coalescence. This property enables circuits that automatically repair cuts, punctures, and other damage that would permanently disable conventional electronics. According to studies in Advanced Functional Materials, properly formulated liquid metal composites can achieve 95% conductivity recovery within seconds of damage, with some systems capable of multiple healing cycles at the same location. Our development focuses on pressure-activated healing systems where encapsulated healing agents are released upon damage, creating conditions that facilitate oxide disruption and liquid metal reconnection. This approach has demonstrated 100% functional recovery after complete circuit severing, creating electronic systems with unprecedented resilience for applications in harsh environments.
What Advanced Applications Demonstrate Transformative Potential?
Liquid metal integrations are enabling entirely new categories of electronic devices that merge seamlessly with biological systems, soft robotics, and reconfigurable electronics.

How Are Biomedical Sensors Revolutionizing Health Monitoring?
Liquid metal biomedical sensors create intimate, long-term interfaces with biological tissues for continuous health monitoring without the discomfort and motion artifacts of conventional rigid sensors. These systems leverage liquid metals' mechanical similarity to biological tissues (Young's modulus ~0.1-1 MPa) to create interfaces that don't provoke foreign body responses or impede natural tissue movement. Research in Nature Medicine demonstrates that liquid metal neural interfaces can maintain stable recording quality for months compared to weeks for conventional rigid electrodes, due to reduced micromotion and tissue damage. Our development focuses on multi-modal sensors that combine electrical, thermal, and mechanical sensing in single, minimally invasive devices. These systems have demonstrated continuous cardiovascular monitoring with clinical-grade accuracy during normal daily activities, overcoming the limitations of current wearable monitors that lose accuracy during movement.
Can Reconfigurable Electronics Enable Adaptive Systems?
Liquid metal's fluid nature enables truly reconfigurable electronics where circuit paths can be dynamically created, modified, or erased on demand. These systems use electrochemical, thermal, or mechanical actuation to manipulate liquid metal patterns within microfluidic networks, creating electronics that can adapt their function to changing requirements. Studies in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences show that properly designed reconfigurable systems can implement different circuit functions (filters, antennas, sensors) using the same physical hardware by reprogramming liquid metal patterns. Our implementation uses electrowetting-based control that positions liquid metal droplets with 10 μm precision, creating field-programmable devices that can switch between sensing, communication, and power management functions. This approach has particular promise for wearable systems where size and weight constraints make dedicated hardware for each function impractical.
What Manufacturing and Reliability Considerations Impact Commercial Viability?
Successful commercialization of liquid metal circuits requires addressing manufacturing scalability, long-term reliability, and integration with conventional electronic components.
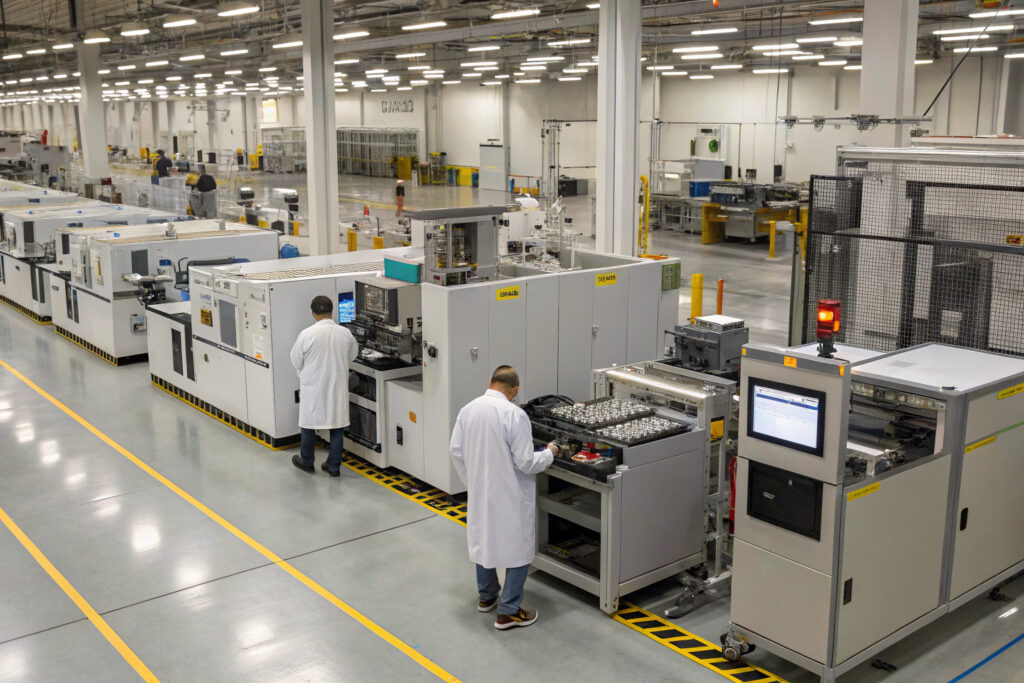

How Can Scalable Manufacturing Be Achieved?
Scalable manufacturing of liquid metal circuits requires approaches that balance speed, resolution, and yield across large areas. Roll-to-roll compatible methods including gravure printing, flexographic patterning, and continuous injection molding have emerged as the most promising approaches for high-volume production. According to analysis by the FlexTech Alliance, optimized roll-to-roll processes can achieve production speeds of 1-5 m/min with feature sizes of 50-200 μm, making liquid metal circuits economically viable for consumer applications. Our manufacturing approach uses modified screen printing with oxide-stabilized liquid metal inks that achieve 25 μm feature sizes at speeds compatible with textile manufacturing processes. The process achieves 95% first-pass yield with electrical performance variation below 5% across production batches, meeting requirements for commercial electronic applications.
What Reliability Measures Ensure Long-Term Performance?
Liquid metal circuits require specific reliability considerations including gallium interaction with other metals, oxide accumulation, and encapsulation integrity under mechanical stress. Comprehensive reliability assessment must address:
- Intermetallic formation with contact metals (copper, gold)
- Oxide skin growth and its impact on electrical and mechanical properties
- Encapsulation material stability and adhesion through environmental exposure
- Performance maintenance through mechanical cycling and temperature variations
Research in IEEE Transactions on Components, Packaging and Manufacturing Technology demonstrates that properly engineered liquid metal systems can maintain stable performance for 5+ years in wearable applications when protected from direct environmental exposure and mechanical abrasion. Our reliability program includes accelerated testing equivalent to 10 years of use, with systems demonstrating resistance changes below 15% and mechanical integrity maintained through 1 million deformation cycles. This reliability level enables applications in medical devices, safety equipment, and consumer electronics where failure is not an option.
Conclusion
Liquid metal circuit integrations represent a paradigm shift in electronic design, enabling systems that are soft, stretchable, self-healing, and reconfigurable—properties impossible with conventional rigid electronics. The most advanced implementations combine sophisticated patterning techniques, unique material properties, and innovative applications to create electronic systems that seamlessly integrate with biological systems, soft robots, and adaptive devices. As manufacturing methods advance and reliability understanding deepens, liquid metal circuits are transitioning from laboratory demonstrations to commercial products across healthcare, wearable technology, and soft robotics.
Ready to explore liquid metal circuit integrations for your electronic systems? Contact our Business Director, Elaine, at elaine@fumaoclothing.com to discuss how liquid metal technology can enable new product categories and enhance existing designs with unprecedented flexibility and durability. Our materials science and electronics teams have direct experience with multiple liquid metal platforms and can help develop optimized integration strategies for your specific application requirements.