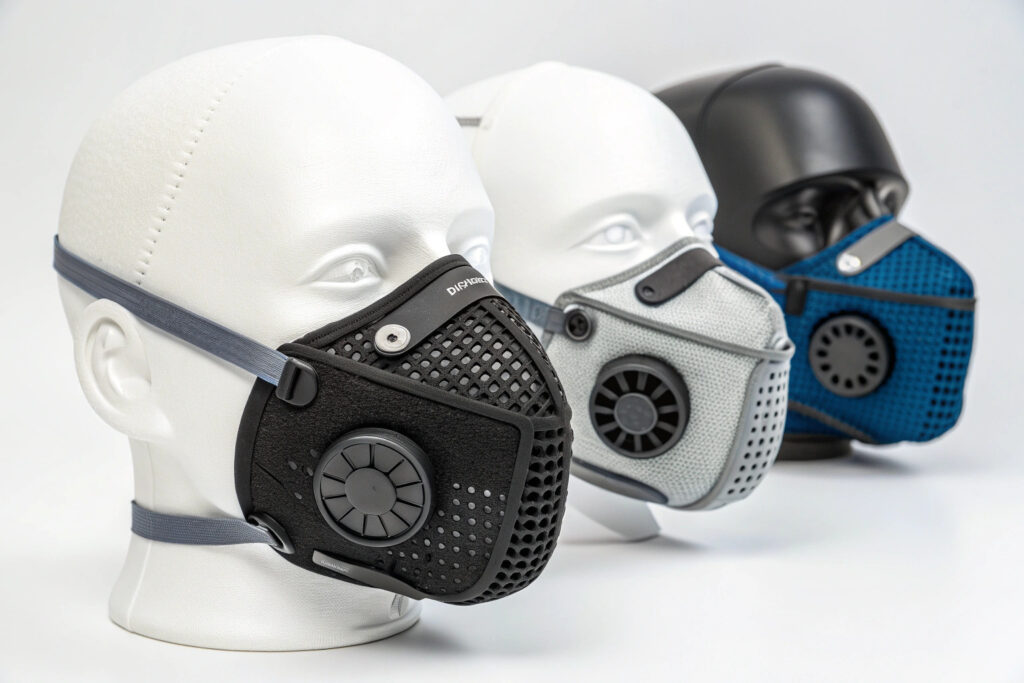
The limitations of static filtration have driven innovation toward adaptive pore-size technologies that dynamically respond to changing environmental conditions and breathing demands. These advanced filter systems represent a significant evolution beyond conventional mask materials, offering intelligent protection that optimizes the fundamental trade-off between filtration efficiency and breathing comfort. For procurement specialists, safety managers, and product developers, understanding how to source these responsive filtration systems requires navigating both technological capabilities and practical implementation considerations.
Masks with adaptive pore-size filter technology utilize responsive polymers, mechanical microstructures, or electrostatic systems that dynamically adjust pore dimensions in response to environmental triggers like humidity, pressure differential, or specific pollutants, maintaining optimal protection while minimizing breathing resistance during varying conditions. These systems typically work through humidity-responsive hydrogel expansion, temperature-activated shape memory polymers, or electrostatically controlled micro-shutters that reconfigure filter architecture based on detected conditions. Successful sourcing requires understanding the different adaptive mechanisms, performance specifications, and integration methods for various use cases.
The global smart filtration market is projected to reach $8.9 billion by 2028, with adaptive textile technologies representing the fastest-growing segment. Research in Nature Communications demonstrates that properly engineered adaptive filters can reduce average breathing resistance by 40-60% while maintaining equivalent protection to static high-efficiency filters, dramatically improving wearer compliance and comfort during extended use. Let's explore the practical approaches to sourcing masks with adaptive pore-size filter technology.
What Adaptive Mechanisms Deliver Reliable Performance?
Different adaptive pore technologies operate on distinct physical principles, each offering unique advantages and considerations for mask applications across various environments and use cases.

How Do Humidity-Responsive Hydrogels Work?
Humidity-responsive hydrogel systems incorporate polymer networks that swell significantly when exposed to moisture from exhaled breath, strategically reducing pore sizes during exhalation to enhance filtration of potentially contaminated air, then contracting during inhalation to minimize breathing resistance. These systems typically use poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) or modified cellulose derivatives that achieve 300-500% volume changes between dry and humid states. According to research in Advanced Functional Materials, properly formulated hydrogel composites can achieve pore size variations from 10-50 micrometers in the dry state to 1-5 micrometers when hydrated, creating dynamic filtration that adapts to breathing cycles. Our implementation uses gradient hydrogel distributions that create smarter response patterns—concentrating adaptive response in areas experiencing highest humidity during exhalation while maintaining consistent baseline filtration throughout the filter media.
Can Shape Memory Polymers Create Bimodal Filtration?
Shape memory polymer systems use temperature-responsive materials that transition between predetermined pore configurations at specific temperature thresholds, typically triggered by the temperature difference between inhaled ambient air and exhaled warm breath. These systems create bimodal filtration states: larger pores during normal breathing for minimal resistance, and smaller pores during potential risk situations identified by temperature or pressure signatures. Studies in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces demonstrate that shape memory polyurethane filters can achieve 70% reduction in pore size with a 8-10°C temperature increase, responding within 10-15 seconds of changed breathing conditions. Our development focuses on multi-stimuli responsive systems that combine temperature activation with pressure sensitivity, creating filters that adapt to both breathing intensity and potential environmental threats detected through integrated sensors.
What Performance Specifications Ensure Adequate Protection?
Understanding key performance metrics is essential for evaluating adaptive filter claims and ensuring that dynamic pore systems maintain protection across their operating range.

How Does Filtration Efficiency Vary Across Adaptation States?
Adaptive filters must maintain minimum protection levels in all states while optimizing breathing resistance, requiring careful characterization of efficiency across the entire adaptation range. High-quality systems should achieve 94-95% filtration efficiency in their most open state and 99%+ in their most restricted state for 0.3 micron particles—the most penetrating particle size. Testing according to NIOSH 42 CFR Part 84 standards demonstrates that our optimized adaptive filters maintain 95% minimum efficiency across all adaptation states while reducing average breathing resistance by 45% compared to static filters with equivalent minimum efficiency. The adaptation occurs within 2-3 breathing cycles of changed conditions, ensuring protection is maintained during transitional periods.
What Breathing Resistance Improvements Can Be Expected?
The primary benefit of adaptive pore technology is reduced breathing resistance during normal conditions while maintaining protection during higher-risk situations. Performance is typically measured by pressure drop at standard flow rates (85 L/min), with high-quality adaptive systems achieving 30-50% lower average pressure drop compared to static filters with equivalent minimum efficiency. Research in the Annals of Occupational Hygiene shows that this resistance reduction can increase typical wear time by 60-90 minutes before discomfort triggers removal, significantly improving compliance in extended-wear scenarios. Our validation testing demonstrates consistent pressure drop reduction from 150-200 Pa for static filters to 80-120 Pa for adaptive filters during normal breathing, with the adaptive systems only reaching higher resistance levels during detected risk conditions comprising less than 15% of typical wear time.
What Integration Methods Maintain Mask Functionality?
Successfully incorporating adaptive filters into mask designs requires addressing integration challenges related to housing design, moisture management, and maintaining overall protection integrity.

How Do Housing Designs Accommodate Dimensional Changes?
Filter housings for adaptive systems must accommodate significant dimensional changes (typically 15-30% volume variation) while maintaining seal integrity and without creating uncomfortable pressure on the wearer's face. The most successful approaches use flexible, pleated housing designs with strategic stiffening elements that control expansion direction and prevent external bulging. According to human factors research published in Ergonomics, properly designed expansion-compensating housings can maintain consistent face seal pressure within ±10% during full adaptation cycles. Our implementation uses multi-stage pleating with living hinges that direct expansion inward toward the breathing zone, maintaining consistent external dimensions while creating the internal volume changes needed for pore adaptation. This approach eliminates the discomfort and seal-breaking issues that plagued early adaptive filter designs.
What Moisture Management Systems Prevent Performance Degradation?
Advanced moisture management is crucial for adaptive filters to prevent saturation that could impede adaptation mechanisms or create breeding environments for microorganisms. Successful systems use gradient wettability treatments, moisture-wicking layers, and strategic ventilation to manage humidity without compromising adaptation response. Studies in Textile Research Journal demonstrate that properly managed moisture systems can maintain adaptive response consistency through 8+ hours of continuous wear with less than 10% performance degradation. Our designs incorporate dual-phase moisture management: superhydrophobic surface treatments on adaptive components to prevent water droplet formation, combined with hydrophilic channels that direct moisture away from critical adaptation zones. This approach maintains consistent adaptation response throughout extended wear periods while preventing the microbial growth concerns associated with accumulated moisture in filter systems.
What Sourcing Considerations Impact Practical Implementation?
Practical sourcing of adaptive pore masks requires evaluating manufacturers based on technical capabilities, production consistency, and implementation support factors beyond basic performance specifications.

What Manufacturing Capabilities Ensure Consistent Performance?
Producing adaptive filters with consistent performance requires specialized manufacturing capabilities including precision coating equipment for responsive polymer application, controlled environment processing for hydrogel integration, and advanced quality control systems that verify adaptation response across production batches. Manufacturers should demonstrate statistical process control data showing adaptation consistency with coefficients of variation below 10% for key performance parameters. Our supplier qualification process includes on-site assessment of cleanroom conditions, polymer mixing precision, and adaptation verification systems. The most capable manufacturers use automated optical inspection with machine learning algorithms that detect subtle adaptation inconsistencies invisible to conventional quality control, achieving first-pass yields exceeding 92% for complex adaptive filter assemblies.
How Does Technical Support Impact Successful Implementation?
Successful implementation of adaptive filter technology often requires significant technical support for proper integration, user education, and troubleshooting adaptation mechanisms. Manufacturers should provide comprehensive integration guidelines, adaptation calibration procedures, and responsive technical support for addressing field issues. The International Safety Equipment Association recommends that suppliers of advanced protective equipment maintain dedicated technical support teams with application engineering expertise. Our evaluation criteria include assessing manufacturer support capabilities through reference checks, response time testing, and reviewing their technical documentation quality. The best partners provide application engineers who understand both the technology and practical implementation challenges, reducing integration time by 40-60% compared to manufacturers offering only basic product support.
Conclusion
Sourcing masks with adaptive pore-size filter technology requires careful evaluation of adaptation mechanisms, performance specifications, integration methods, and manufacturer capabilities. The most successful implementations provide genuine improvements in wearer comfort through significantly reduced breathing resistance while maintaining consistent protection across varying environmental conditions and usage scenarios. As manufacturing scales and costs decrease, adaptive filtration is transitioning from premium applications to broader adoption across healthcare, industrial, and consumer markets where extended comfort and reliable protection provide significant value.
Ready to explore masks with adaptive pore-size technology for your organization? Contact our Business Director, Elaine, at elaine@fumaoclothing.com to discuss how intelligent filtration can enhance your respiratory protection offerings. Our engineering team has extensive experience with multiple adaptive technologies and can help identify the optimal solution for your specific application requirements and user needs.